#china
Text
Grandma's underground secret courtyard (nainai's underground beautiful chinese yuanzi) by 杨道友的探索旅行
#china#video#xhs#douyin#aesthetics#it's northern chinese style#soothing music#chinese countryside#architecture
660 notes
·
View notes
Text
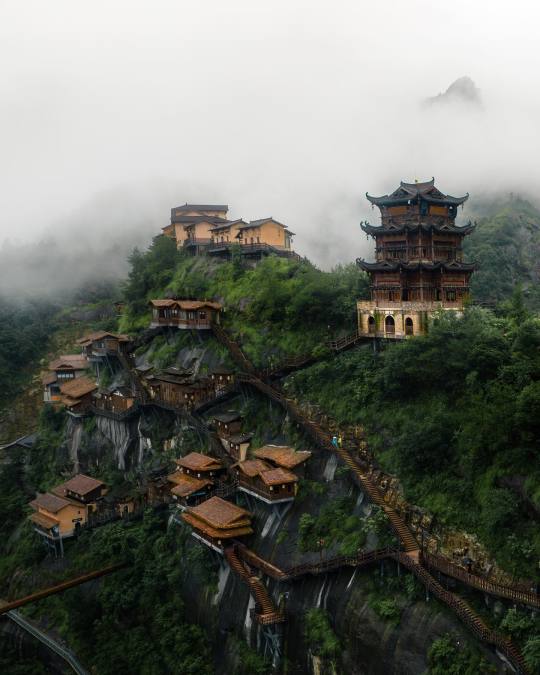
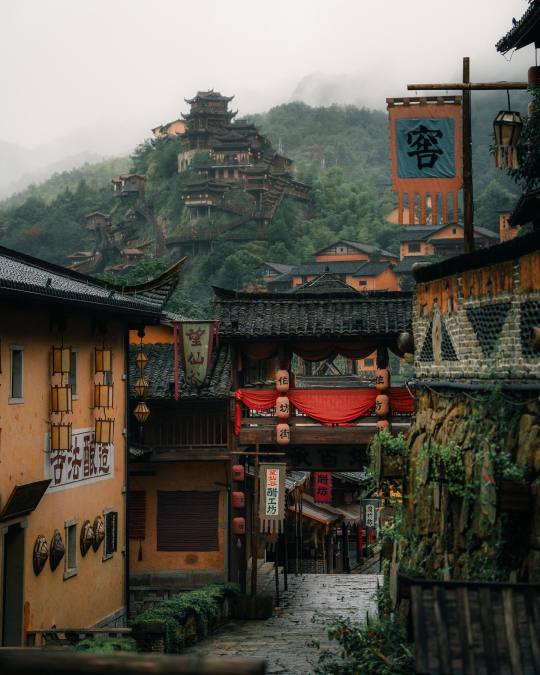
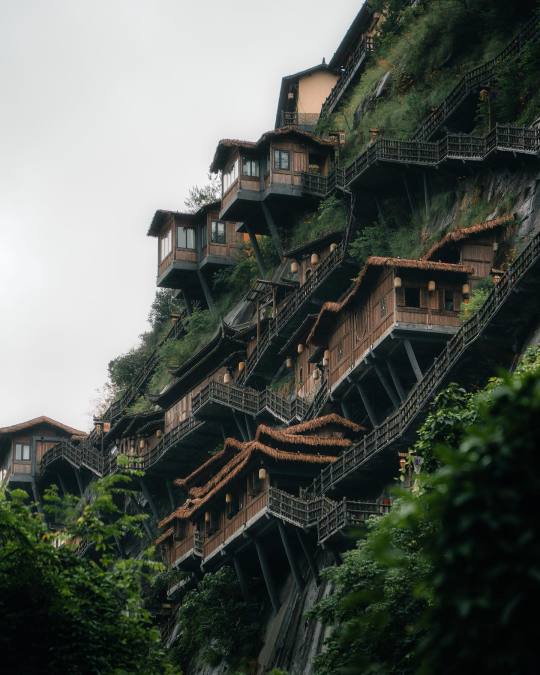
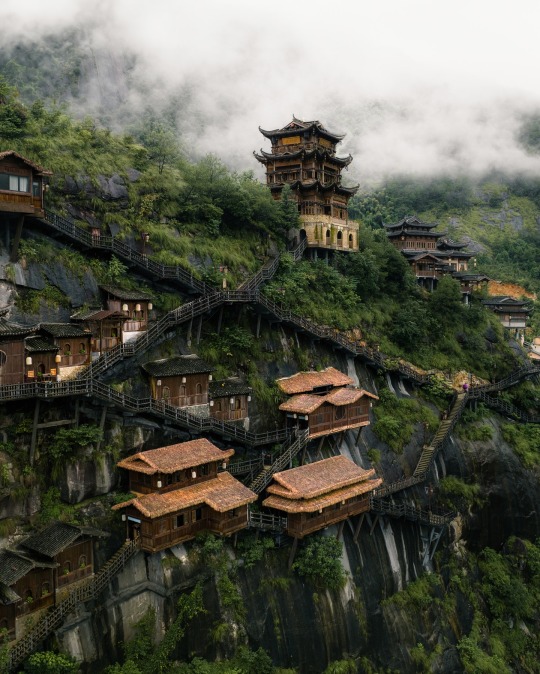




Wangxian Valley, Shangrao City, Jiangxi Province
long.explorer
471 notes
·
View notes
Text




chinese hanfu
329 notes
·
View notes
Text
a glance of chines scenery
277 notes
·
View notes
Text
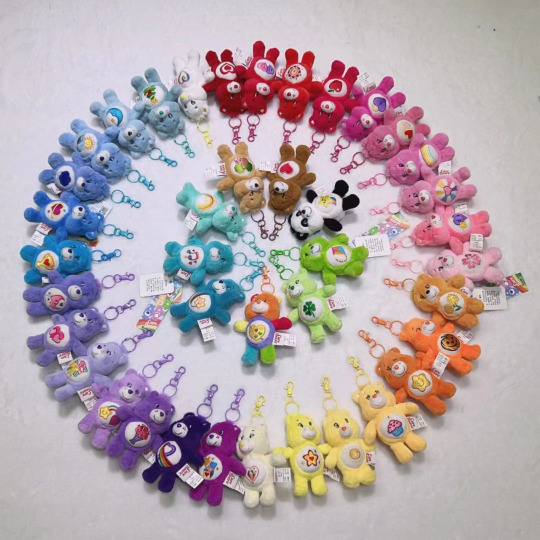

Just saw this image on a Taobao listing. Looks like the Chinese Care Bears keychain set is about to expand significantly! (Twenty of these bears were already available and there are twenty new ones in the pic.)
#Care Bears#plushies#China#Taobao#bears I'm especially excited about:#Trick or Sweet Bear#Sea Friend Bear#Wish Bear#Bedtime Bear#Good Luck Bear#Sparkle Heart Bear#also can we just appreciate that every bear is a slightly different shade if you look at all the pink ones or all the blue ones etc
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
Abnormally warm patches of water in the Pacific Ocean, often referred to as 'blobs', have been having a disastrous effect on marine ecosystems since 2010. Now we may know what's causing them to keep appearing.
A new study from an international team of researchers, and involving some detailed computer simulations, has linked the blobs to a reduction in aerosol emissions in China – so a policy designed to improve environmental conditions may have also come with negative consequences attached.
The reason is that these tiny airborne particles released by factories and power plants do a very good job at reflecting sunlight back into space, and keeping our atmosphere cooler.
Without that cover, the Pacific is more exposed to heat from the Sun, which combines with increasing heat from human-made global warming.
Continue Reading.
74 notes
·
View notes
Text

Canola Flowers Field, China
#china#places#flowers#flower fields#fields#nature#landscapes#landscape#yellow#yellowcore#aesthetic#earthcore#earthy#naturecore
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elon Musk: "China nunca podrá copiar nuestra tecnología"
China:

33 notes
·
View notes
Photo
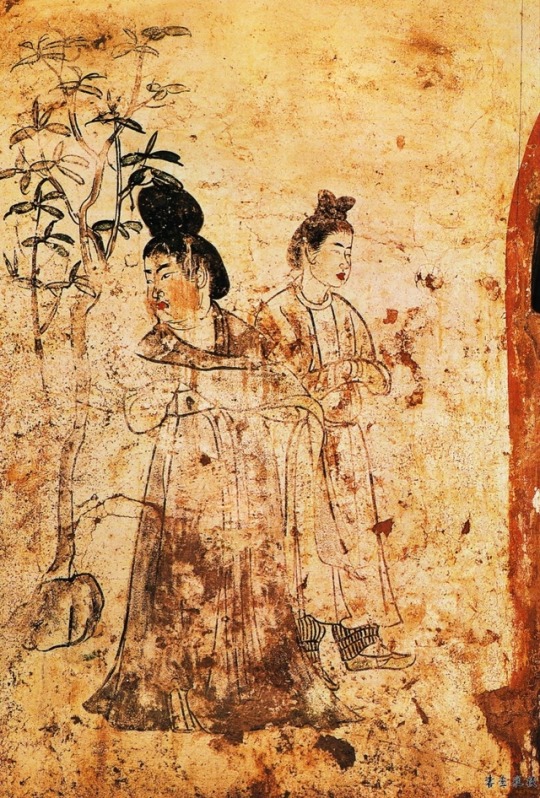
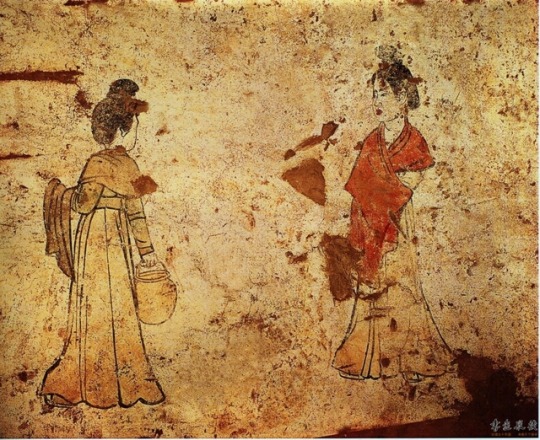
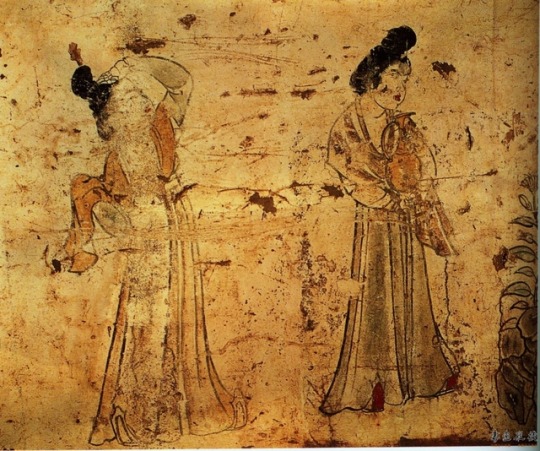
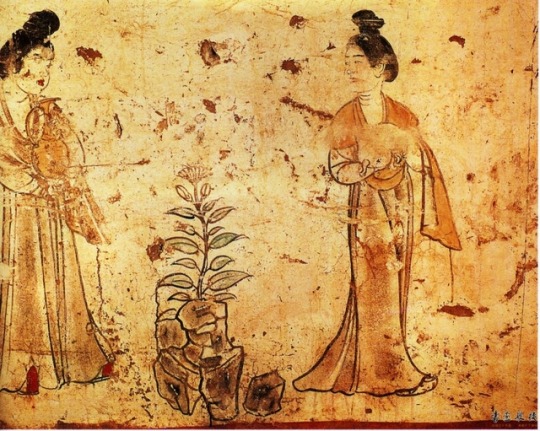
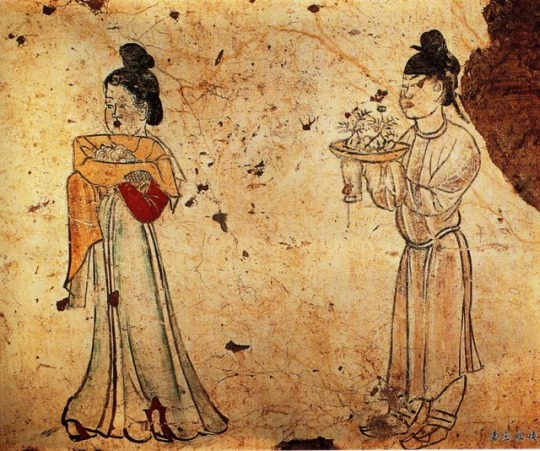
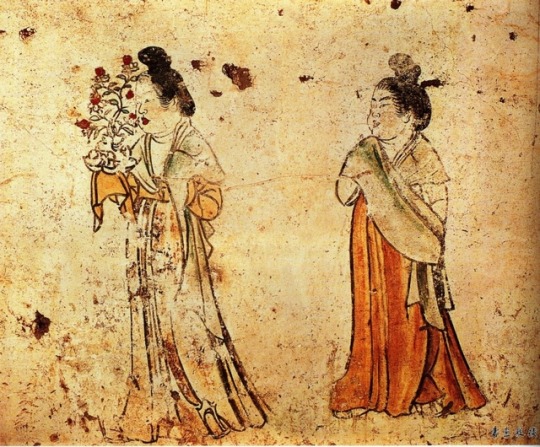










Murals from the tomb of Li Xian Prince Zhanghuai (655--684); Tang Dynasty China
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

. 𝐸𝓂𝓅𝓇𝑒𝓈𝓈 𝒴𝓊𝒶𝓃 𝒮𝒾
33 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sent to a foreign country as a tribute, Lady Ki (c.1320- after 1369) carved a place for herself and became a powerful empress, the last of the Yuan dynasty.
From maid to imperial consort
Lady Ki, also known as Öljei Khuduq, was born in Xingzhou, Gaoli (present-day Korea). The Korean state used to send a tribute of women to its neighbor, the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty, who controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas such as present-day Mongolia.
Lady Ki entered the palace and was assigned to Toghon Temür's service. Described as beautiful and clever, she quickly caught the young emperor’s attention and was elevated to the rank of consort.
The empress Danishiri was hostile to Lady Ki but was executed in 1335 or 1337 for having tried to protect her brother who was involved in a rebellion.
Toghon Temür then tried to name Lady Ki empress, but his decision was met with extreme hostility. Indeed, no Korean woman had held the dignity so far. Most empresses came from the Mongol Khongirad clan. He ultimately relented and chose a Mongol empress: Bayan Khuduq.
A powerful favorite
Lady Ki’s position was strengthened when she gave birth to a son, Ayushiridara (future emperor Zhaozong of Northern Yuan, r.1370-1378). Bayan Khuduq's son died young. Having a frugal and effaced personality, the empress was furthermore no match for Lady Ki. Ayushiridara was thus made heir apparent in 1355.
Empress Ki was influential and involved herself in political and military affairs. She for instance protected the high-ranking official Toqto'a but withdrew her support when he opposed the installation of her son as heir apparent.
She liked to read the Women’s Book of Filial Piety and sought examples of past empresses she could emulate. When a famine struck in 1359, she showed her generosity by having the officials distribute porridge to the hungry, using her own funds to have thousands of corpses buried and hiring monks to perform funeral services.
Lady Ki used her influence to promote her family’s interests. Her kinsmen in Korea were granted official ranks and titles. They repeatedly abused their power, which led the Korean king to execute Lady Ki’s entire clan.
When she learned about it, she asked her son to avenge her family and raise a force of 10,000 soldiers. The military campaign was a complete failure and the entire force was routed.
Empress before the fall
Bayan Khuduq died in 1365. No obstacles stood in Lady Ki’s way and she received the empress’s seal. It seems that she tried to make up for the mistakes of a poorly-performing emperor. Later historians indeed wrote that Toghon Temür preferred focusing on wine and women, though this could be an exaggeration to justify the fall of the Yuan Dynasty.
The government’s structure was disintegrating. Empress Ki conspired to force the emperor to abdicate and put her son on the throne but failed. She faced little consequences and was simply put under house arrest for 100 days. Her agressive defense of her son’s interests was in keeping with Mongolian political culture, which recognized the influence of strong women.
The Yuan dynasty fell in 1368 when the armies of the future Ming Emperor Hongwu entered the capital. Empress Ki fled to the north with Toghon Temür. What happened to her afterward is unclear, but she likely died the following year.
Her life was the inspiration for a 2013 Korean television drama, Empress Ki.
Feel free to check out my Ko-Fi if you like what I do! Your support would be much appreciated.
Further reading
Buell Paul D., Fiaschetti Francesca, Historical Dictionary of the Mongol World Empire
McMahon Keith, Celestial Women: Imperial Wives and Concubines in China from Song to Qing
Robinson David M., Empire's Twilight: Northeast Asia Under the Mongols
Xu Shindan, “Öljei Qudu”, in: Hong Lee Lily Xiao, Wiles Sue (ed.), Biographical Dictionary of Chinese Women, Volume II: Tang Through Ming 618 - 1644
#empress ki#history#women in history#women's history#historyedit#queens#empresses#powerful women#14th century#korea#korean history#china#chinese history#mongolia#kdramas#historyblr#historical figures#asian history
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
op's ginger cat is missing and she asks for help from the dragon-li in the neighborhood (cr: 如欣如愿)
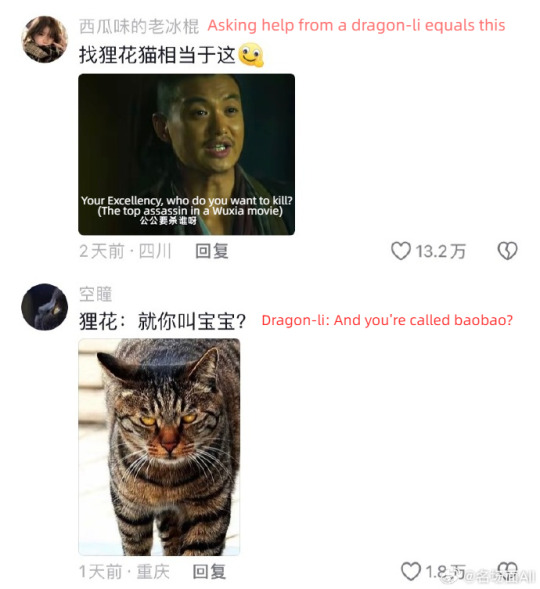
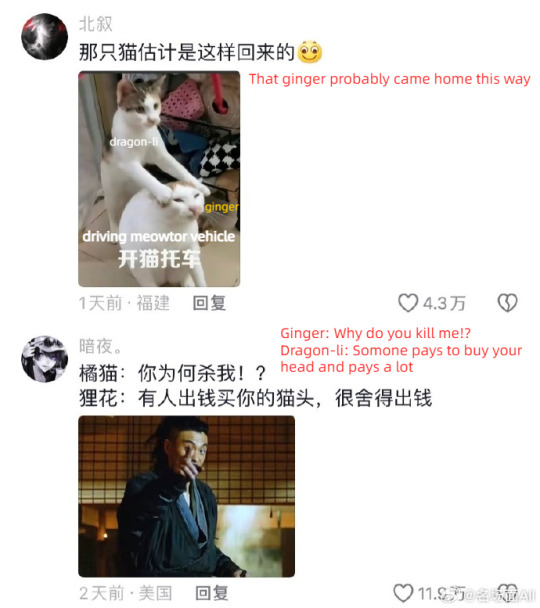
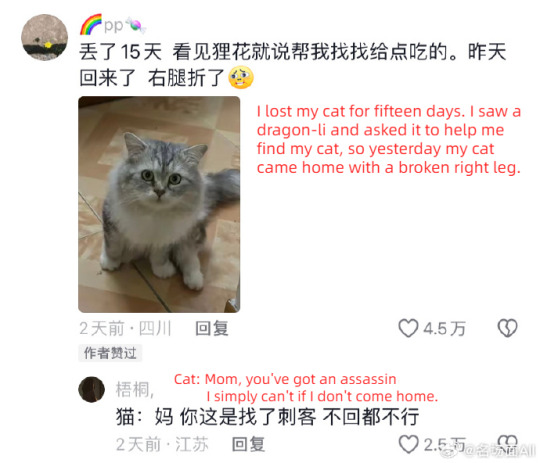
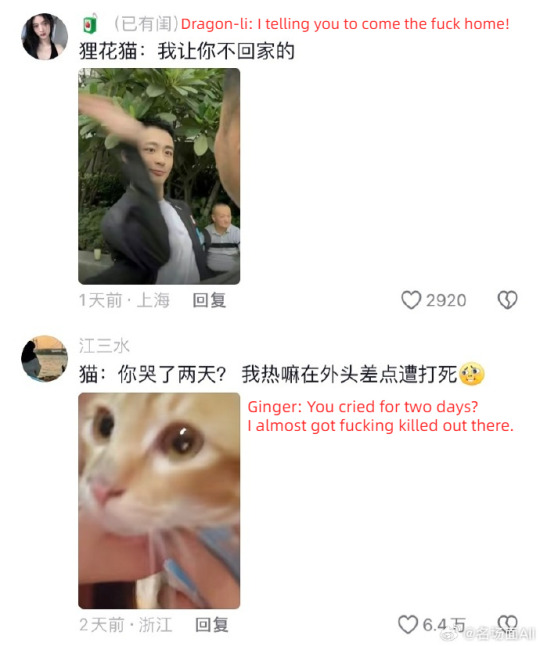
#china#douyin#video#cats#fun#funny#cnetizens have many smart and useful methods to find their missing cats and this is the most popular one#a dragon-li is like the king in the cat neighborhood#dragon-li is not tabby there are differences#it's like a chinese landrace
346 notes
·
View notes
Text

36 notes
·
View notes
Text
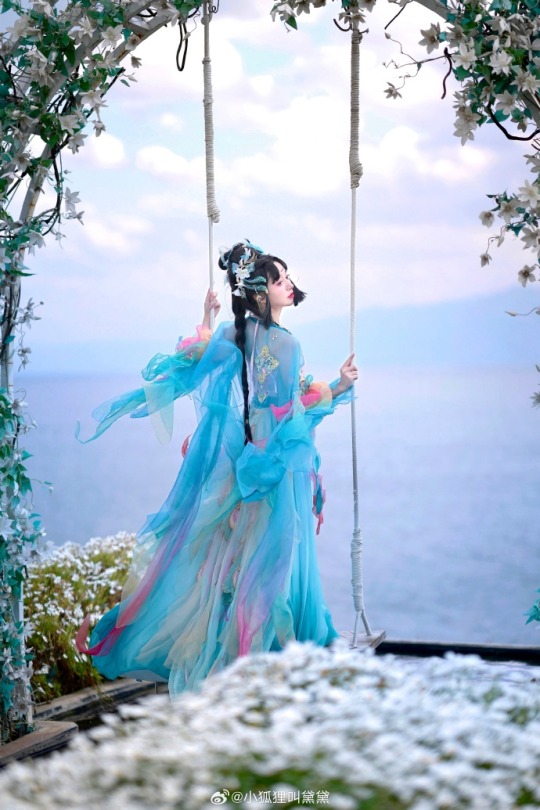
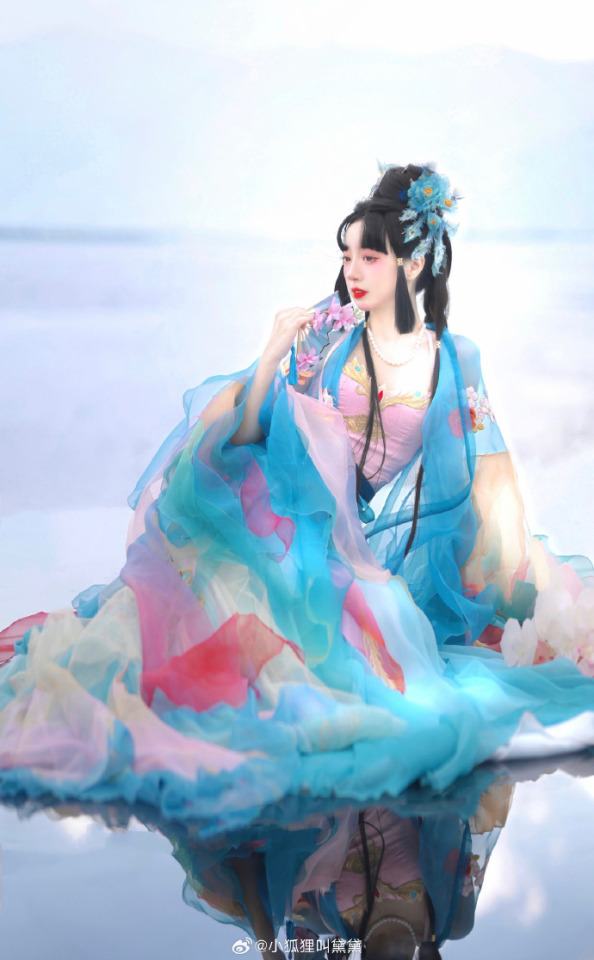
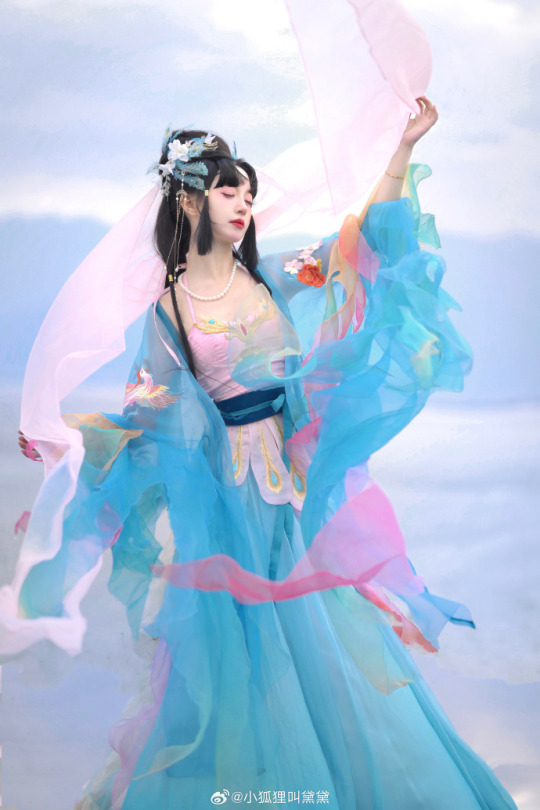
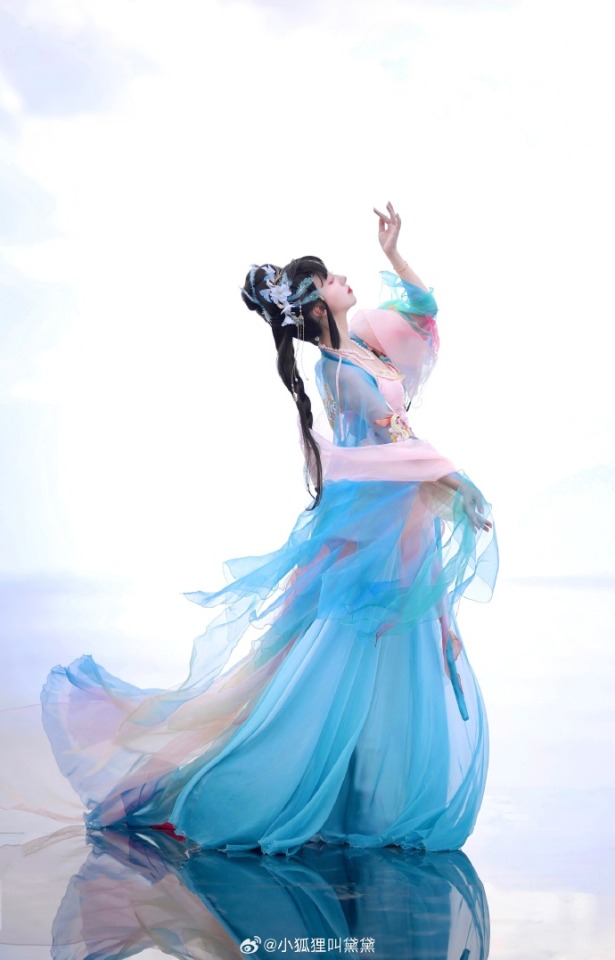
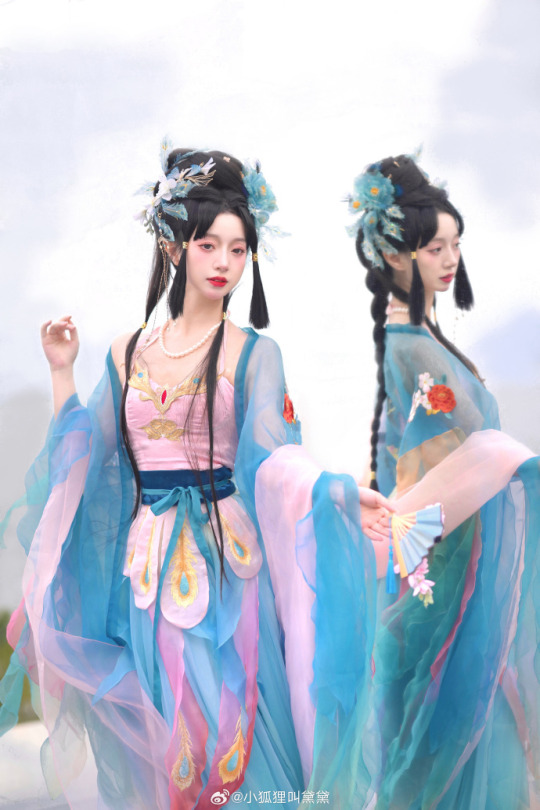
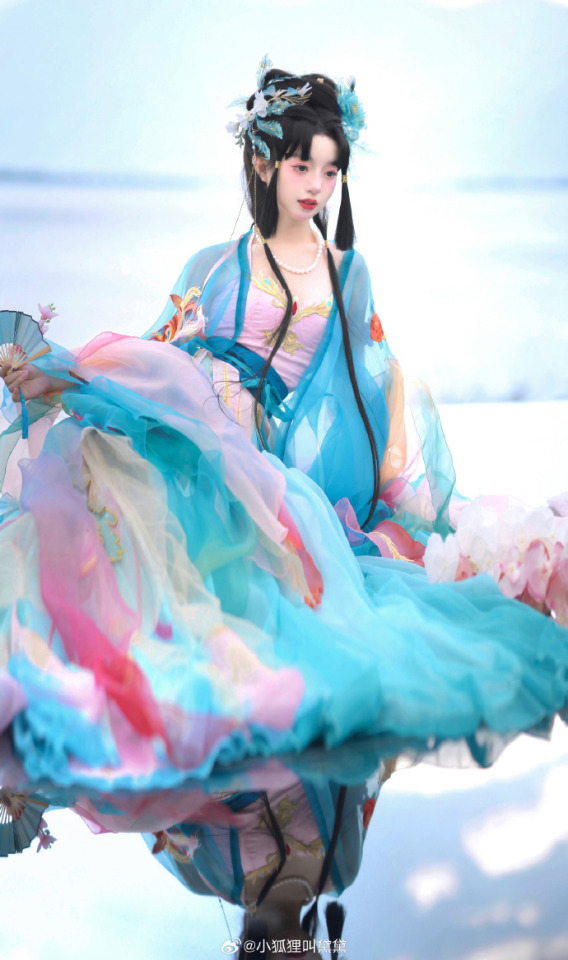
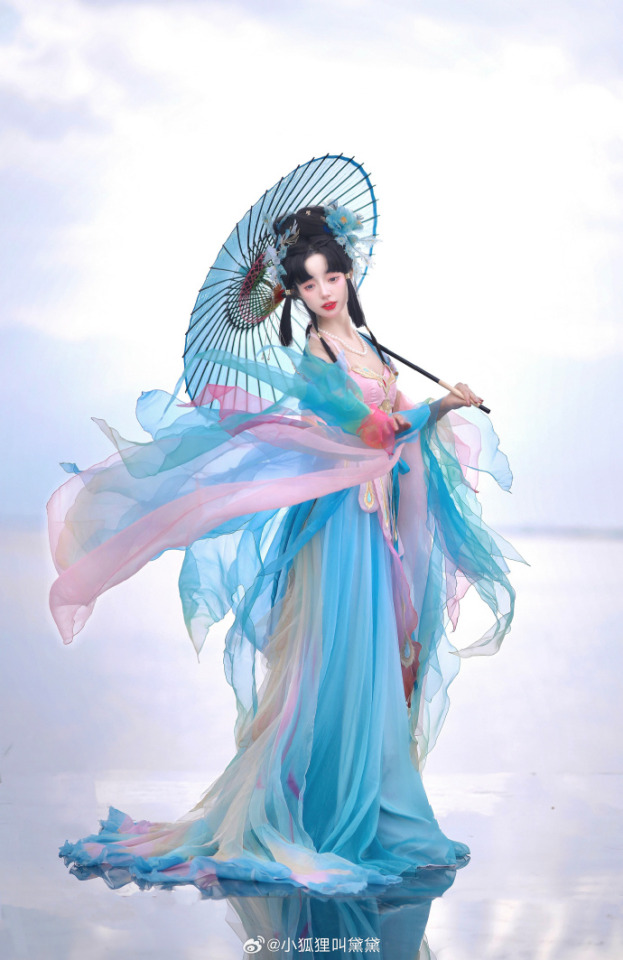








chinese hanfu
136 notes
·
View notes
Text
suzhou garden by 六毛钱的月亮
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Monkey King - Sun Wukong who first appears in Chinese stories (Journey to the West) during the Ming Dynasty period 1368 to 1644 CE, well after the introduction of Buddhism to China in about 206-220 CE.
But, was he inspired by another Monkey hero/character of myth?

The prevailing and dominant theory among Asian scholars is ...yeah, likely.
That character, Hanuman, king of the monkeys (the monkey people -Vanaras- of Vedic myth!).
The story follows a Buddhist monk who is accompanied by Sun Wukong and others to travel west to India to obtain sacred Buddhist sutras. Many of their powers and personality traits are similar as well.
We know that Vedic god such as Indra have made their way as far as Japan to take root and be worshipped because of the spread of Buddhism.
As I've talked about before and is shown in texts such as the journey's of Ibn Battuta / Ibn Fadlan, storytelling was a weapon and powerful tool for idea transfer--propagation. Philosophy was huge in the old world - and places such as Nalanda - the first residential university in the world - invited scholars from all over such as Greeks from the west, and the Japanese. Buddhism became a vehicle for trading things such as: martial arts information, medicine, sciences, and of course, myths and stories.
However, as with stories, people usually altered/coopted elements and molded them to better suit their cultures and fancy. That's a thing as old as time. I've shared how the panchatantra stories and jatka tales are thought to be the inspiration for nearly 30-50 percent of all nursery rhymes, ballads, "fairy tales".
Anyways back to this theory - Chinese Indologist Professor Liu Anwu of Peking University has dedicated chapters to the comparisons (in one of his works) to further break down this theory focusing on consistent and or similar depictions of beats in Journey to the West that of Rama's story in Ramayama and the Buddhist sutras.
Even though today the story of Sun Wukong is a wholly Chinese story - it's important to note the power of oral storytelling and how it travelled evolved over thousands of years, and, just as important, the vehicles it used to do so. Not just storytellers and philosophers and travelers but religion! Philosophy!
This is a theme heavily commented on and shown in Tales of Tremaine, which is my love letter and sort of self PhD. in comparative storytelling, mythology, and story foundry through an Asiatic lens (hence a silk road analog) stretching along a similar route the silk road did from damn near as far as you can east (complete with the oceanic routes) to as west as old venezia, portugal, and spain.
Also note: this is the most popular theory atm, but the operative word is theory. Experts likely far better than you, Internet, so chill before you comment, are still debating this. I know last week some of you were doctors in sociopolitical relations, the music industry before that, and then you were leading virologists before that. Spare us simpler folks from your mighty genius just now and sit down.
The point here is the beauty of stories and their ability to travel and morph and comment on themes/points ideologies important to cultures while being entertaining and showing that humans like certain universal moments, beats, archetypes, tropes, and progressions in tales.
Now, is that because we've naturally been predisposed liking them, or the opposite in that everyone went, yo, i dig this, took it home and someone else went, this is cool but needs to be more US (insert culture) and retold it. And thus...timemachine noises speed up. Here we are today?
You might not know that about 35,000 Chinese words ( I said this instead of Mandarin because they don't just show up in one language) are derived from Sanskrit as well as Pali (a Middle Indo-Aryan Liturgical Language -- meaning language of sacredness/religious use, in this case connected to sacred Buddhist texts). It is important to make the distinction, because, Internet!
Sanskrit did not SHAPE the Chinese languages. They evolved on their own. This is just a commentary on how words/stories shaped over travel in this case strongly through the spread of Buddhism.
Religion was the mover.
Back from quick bathroom break. Going to add again - INSPIRED is the keyword here.
INSPIRED.
Sun Wukong is his own mythos/character. Influence doesn't nor can claim dominion over everything in a later tale. Sun Wukong has gone on himself to inspire legends and characters Outside of China - re: most famously and legendary?
Son Goku - who is openly a Sun Wukong inspired character.
...hell, tbh, he might be the most famous monkey inspired super powered character now. Dude makes soccer stadiums air his fights. @_@.
#monkey king#monkey king journey to the west#hanuman#buddhist#buddhist monk#sun wukong#vedic gods#Japan#China#chinese legend#storytelling#mythology#myths and legends#asian mythology#mandarin#Sanskrit#pali#chinese language#dbz#dragon ball#dragon ball z#inspired#inspired by#the silk road#silk road retelling#philosophy#philosophers#journey to the west#fairy tales#nursery rhymes
25 notes
·
View notes