#disenshittification
Text
Kickstarting a book to end enshittification, because Amazon will not carry it

My next book is The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of Computation: it’s a Big Tech disassembly manual that explains how to disenshittify the web and bring back the old good internet. The hardcover comes from Verso on Sept 5, but the audiobook comes from me — because Amazon refuses to sell my audio:
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/doctorow/the-internet-con-how-to-seize-the-means-of-computation
Amazon owns Audible, the monopoly audiobook platform that controls >90% of the audio market. They require mandatory DRM for every book sold, locking those books forever to Amazon’s monopoly platform. If you break up with Amazon, you have to throw away your entire audiobook library.
That’s a hell of a lot of leverage to hand to any company, let alone a rapacious monopoly that ran a program targeting small publishers called “Project Gazelle,” where execs were ordered to attack indie publishers “the way a cheetah would pursue a sickly gazelle”:
https://www.businessinsider.com/sadistic-amazon-treated-book-sellers-the-way-a-cheetah-would-pursue-a-sickly-gazelle-2013-10

[Image ID: Journalist and novelist Doctorow (Red Team Blues) details a plan for how to break up Big Tech in this impassioned and perceptive manifesto….Doctorow’s sense of urgency is contagious -Publishers Weekly]
I won’t sell my work with DRM, because DRM is key to the enshittification of the internet. Enshittification is why the old, good internet died and became “five giant websites filled with screenshots of the other four” (h/t Tom Eastman). When a tech company can lock in its users and suppliers, it can drain value from both sides, using DRM and other lock-in gimmicks to keep their business even as they grow ever more miserable on the platform.
Here is how platforms die: first, they are good to their users; then they abuse their users to make things better for their business customers; finally, they abuse those business customers to claw back all the value for themselves. Then, they die:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys

[Image ID: A brilliant barn burner of a book. Cory is one of the sharpest tech critics, and he shows with fierce clarity how our computational future could be otherwise -Kate Crawford, author of The Atlas of AI”]
The Internet Con isn’t just an analysis of where enshittification comes from: it’s a detailed, shovel-ready policy prescription for halting enshittification, throwing it into reverse and bringing back the old, good internet.
How do we do that? With interoperability: the ability to plug new technology into those crapulent, decaying platform. Interop lets you choose which parts of the service you want and block the parts you don’t (think of how an adblocker lets you take the take-it-or-leave “offer” from a website and reply with “How about nah?”):
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/07/adblocking-how-about-nah
But interop isn’t just about making platforms less terrible — it’s an explosive charge that demolishes walled gardens. With interop, you can leave a social media service, but keep talking to the people who stay. With interop, you can leave your mobile platform, but bring your apps and media with you to a rival’s service. With interop, you can break up with Amazon, and still keep your audiobooks.
So, if interop is so great, why isn’t it everywhere?
Well, it used to be. Interop is how Microsoft became the dominant operating system:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/adversarial-interoperability-reviving-elegant-weapon-more-civilized-age-slay

[Image ID: Nobody gets the internet-both the nuts and bolts that make it hum and the laws that shaped it into the mess it is-quite like Cory, and no one’s better qualified to deliver us a user manual for fixing it. That’s The Internet Con: a rousing, imaginative, and accessible treatise for correcting our curdled online world. If you care about the internet, get ready to dedicate yourself to making interoperability a reality. -Brian Merchant, author of Blood in the Machine]
It’s how Apple saved itself from Microsoft’s vicious campaign to destroy it:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/adversarial-interoperability-reviving-elegant-weapon-more-civilized-age-slay
Every tech giant used interop to grow, and then every tech giant promptly turned around and attacked interoperators. Every pirate wants to be an admiral. When Big Tech did it, that was progress; when you do it back to Big Tech, that’s piracy. The tech giants used their monopoly power to make interop without permission illegal, creating a kind of “felony contempt of business model” (h/t Jay Freeman).
The Internet Con describes how this came to pass, but, more importantly, it tells us how to fix it. It lays out how we can combine different kinds of interop requirements (like the EU’s Digital Markets Act and Massachusetts’s Right to Repair law) with protections for reverse-engineering and other guerrilla tactics to create a system that is strong without being brittle, hard to cheat on and easy to enforce.
What’s more, this book explains how to get these policies: what existing legislative, regulatory and judicial powers can be invoked to make them a reality. Because we are living through the Great Enshittification, and crises erupt every ten seconds, and when those crises occur, the “good ideas lying around” can move from the fringes to the center in an eyeblink:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/12/only-a-crisis/#lets-gooooo

[Image ID: Thoughtfully written and patiently presented, The Internet Con explains how the promise of a free and open internet was lost to predatory business practices and the rush to commodify every aspect of our lives. An essential read for anyone that wants to understand how we lost control of our digital spaces and infrastructure to Silicon Valley’s tech giants, and how we can start fighting to get it back. -Tim Maughan, author of INFINITE DETAIL]
After all, we’ve known Big Tech was rotten for years, but we had no idea what to do about it. Every time a Big Tech colossus did something ghastly to millions or billions of people, we tried to fix the tech company. There’s no fixing the tech companies. They need to burn. The way to make users safe from Big Tech predators isn’t to make those predators behave better — it’s to evacuate those users:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/18/urban-wildlife-interface/#combustible-walled-gardens
I’ve been campaigning for human rights in the digital world for more than 20 years; I’ve been EFF’s European Director, representing the public interest at the EU, the UN, Westminster, Ottawa and DC. This is the subject I’ve devoted my life to, and I live my principles. I won’t let my books be sold with DRM, which means that Audible won’t carry my audiobooks. My agent tells me that this decision has cost me enough money to pay off my mortgage and put my kid through college. That’s a price I’m willing to pay if it means that my books aren’t enshittification bait.
But not selling on Audible has another cost, one that’s more important to me: a lot of readers prefer audiobooks and 9 out of 10 of those readers start and end their searches on Audible. When they don’t find an author there, they assume no audiobook exists, period. It got so bad I put up an audiobook on Amazon — me, reading an essay, explaining how Audible rips off writers and readers. It’s called “Why None of My Audiobooks Are For Sale on Audible”:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/25/can-you-hear-me-now/#acx-ripoff

[Image ID: Doctorow has been thinking longer and smarter than anyone else I know about how we create and exchange value in a digital age. -Douglas Rushkoff, author of Present Shock]
To get my audiobooks into readers’ ears, I pre-sell them on Kickstarter. This has been wildly successful, both financially and as a means of getting other prominent authors to break up with Amazon and use crowdfunding to fill the gap. Writers like Brandon Sanderson are doing heroic work, smashing Amazon’s monopoly:
https://www.brandonsanderson.com/guest-editorial-cory-doctorow-is-a-bestselling-author-but-audible-wont-carry-his-audiobooks/
And to be frank, I love audiobooks, too. I swim every day as physio for a chronic pain condition, and I listen to 2–3 books/month on my underwater MP3 player, disappearing into an imaginary world as I scull back and forth in my public pool. I’m able to get those audiobooks on my MP3 player thanks to Libro.fm, a DRM-free store that supports indie booksellers all over the world:
https://blog.libro.fm/a-qa-with-mark-pearson-libro-fm-ceo-and-co-founder/
Producing my own audiobooks has been a dream. Working with Skyboat Media, I’ve gotten narrators like @wilwheaton, Amber Benson, @neil-gaiman and Stefan Rudnicki for my work:
https://craphound.com/shop/

[Image ID: “This book is the instruction manual Big Tech doesn’t want you to read. It deconstructs their crummy products, undemocratic business models, rigged legal regimes, and lies. Crack this book and help build something better. -Astra Taylor, author of Democracy May Not Exist, but We’ll Miss It When Its Gone”]
But for this title, I decided that I would read it myself. After all, I’ve been podcasting since 2006, reading my own work aloud every week or so, even as I traveled the world and gave thousands of speeches about the subject of this book. I was excited (and a little trepedatious) at the prospect, but how could I pass up a chance to work with director Gabrielle de Cuir, who has directed everyone from Anne Hathaway to LeVar Burton to Eric Idle?
Reader, I fucking nailed it. I went back to those daily recordings fully prepared to hate them, but they were good — even great (especially after my engineer John Taylor Williams mastered them). Listen for yourself!
https://archive.org/details/cory_doctorow_internet_con_chapter_01
I hope you’ll consider backing this Kickstarter. If you’ve ever read my free, open access, CC-licensed blog posts and novels, or listened to my podcasts, or come to one of my talks and wished there was a way to say thank you, this is it. These crowdfunders make my DRM-free publishing program viable, even as audiobooks grow more central to a writer’s income and even as a single company takes over nearly the entire audiobook market.
Backers can choose from the DRM-free audiobook, DRM-free ebook (EPUB and MOBI) and a hardcover — including a signed, personalized option, fulfilled through the great LA indie bookstore Book Soup:
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/doctorow/the-internet-con-how-to-seize-the-means-of-computation
What’s more, these ebooks and audiobooks are unlike any you’ll get anywhere else because they are sold without any terms of service or license agreements. As has been the case since time immemorial, when you buy these books, they’re yours, and you are allowed to do anything with them that copyright law permits — give them away, lend them to friends, or simply read them with any technology you choose.
As with my previous Kickstarters, backers can get their audiobooks delivered with an app (from libro.fm) or as a folder of MP3s. That helps people who struggle with “sideloading,” a process that Apple and Google have made progressively harder, even as they force audiobook and ebook sellers to hand over a 30% app tax on every dollar they make:
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/doctorow/red-team-blues-another-audiobook-that-amazon-wont-sell/posts/3788112
Enshittification is rotting every layer of the tech stack: mobile, payments, hosting, social, delivery, playback. Every tech company is pulling the rug out from under us, using the chokepoints they built between audiences and speakers, artists and fans, to pick all of our pockets.
The Internet Con isn’t just a lament for the internet we lost — it’s a plan to get it back. I hope you’ll get a copy and share it with the people you love, even as the tech platforms choke off your communities to pad their quarterly numbers.

Next weekend (Aug 4-6), I'll be in Austin for Armadillocon, a science fiction convention, where I'm the Guest of Honor:
https://armadillocon.org/d45/

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this thread to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/31/seize-the-means-of-computation/#the-internet-con

[Image ID: My forthcoming book 'The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of Computation' in various editions: Verso hardcover, audiobook displayed on a phone, and ebook displayed on an e-ink reader.]
#pluralistic#trustbusting#big tech#gift guide#kickstarter#the internet con#books#audiobooks#enshitiffication#disenshittification#crowdfunders#seize the means of computation#audible#amazon#verso
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
Google without AI or ads? Yes!
Google added a new search filter that strips out the ads, the AI, and everything except the basic search results.
The filter is: &udm=14
You can type in the new filter into the google search bar, or you can use the website someone made that basically does that part for you (turn it into your default search engine perhaps).
The website is udm14.com (use .org instead, if you want to filter out NSFW results)
.
A search filter is text you add to a search to customize the results, such as using
-site:twitter.com
to remove all search results with a twitter URL or
filetype:pdf
if you only want links to PDF files.
#google#no ai#anti ai#enshittification#disenshittification#search filters#tech news#search engines#internet
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
I made a thing. Here’s hoping it helps you with your next Google search.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you haven't heard, Google built a bit of a backdoor to access Google without some of the enshittification that's happened over the past 10 years. Not ALL of it, obviously, but at least the AI is gone.
It's easy to set this as your default search engine in your browser's settings if that's what you want to do.
342 notes
·
View notes
Text
for you ppl who really need google bc duckduckgo doesn't cut it, there is an AI free search you can do if you know how to, but also you can use this link:
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Meanwhile, in Brickland
Cory Doctorow:
Analog companies can raise their prices, or worsen next year's model of their products. *Digital* businesses can *travel back in time* and raise the price of something you already own, but need to pay a "subscription" fee for. They can reach back in time and remove features you've already paid for. They can even go back in time and take away things you already own. The omniflexible, omnipresent digital tether between a device and its manufacturer creates *so many* urges that they can't resist:
Are you one of 4,000,000 people who built "smart home" products from Wink into your walls, ceiling and foundation slab at any time since they started shipping in 2014? Surprise! Now you have to pay a "subscription" for all of those gadgets or they'll *brick your fucking house*:
Did you buy a "Mellow Sous Vide" gadget? Surprise, it now costs $48/year to use that gadget!
Did you buy an Exogen ultrasound device to stimulate bone growth after a fracture? Surprise, it bricks itself after you've used it 343 times! Enjoy your e-waste, Hopalong!
Did you *buy a Ferrari performance sports-car*? Surprise, it bricks itself if it detects "tampering" - and the only way to un-brick it is to connect it to the internet, so you'd better hope it doesn't brick itself deep in an underground parking garage. Oops!
Did you buy a Peloton treadmill? Surprise, your $3,000 "smart" treadmill no longer works in standalone mode - unless you pay $480/year, that treadmill is now a clothes-drying rack:
Did you buy an Epson printer? Surprise! It will brick itself after you print a certain number of pages, *for your own good*, because otherwise its ink-sponges might leak:
Did you get - no, wait for it - *did you get a neural implant?* Surprise. The company's new owners don't want to continue supporting your implant, and they won't let anyone else do so either. So now, *part of your brain* has been bricked:
This is like a lifetime money-back guarantee - *for companies*. Any company that experience's seller's remorse can cancel or alter the transaction, retroactively. It's as if Darth Vader opened an MBA program whose only lesson was *I am altering the deal. Pray I don't alter it further":
Darth Vader has the Force. Corporate enshittifiers have something even more powerful: IP law. Companies can cleverly arrange overlapping layers of IP - anticircumvention, trademark, patent, trade secrecy, terms of service, cybersecurity law, contracts - to criminalize otherwise legal activity, like reverse-engineering, jailbreaking, creating alternative clients or third-party parts:
That means that companies know that they can enshittify to their heart's content without fearing a competitor's disenshittification products. Raise the price of ink all you want, because you've figured out how to criminalize generic ink cartridges:
That's a lesson Spotify took to heart. Aaaallll the way back in 2022, Spotify started selling $90 "Car Thing" tablets - little car-vent-mounted gadgets that made it slightly easier to connect your car stereo to your Spotify account. Now that a suitable interval has gone by, Spotify has decided to remotely brick every one of these solid-state devices, no later than December of 2024:
Now, this may seem like a loss to all those Car Thing owners, who are out $90. But consider this: our descendants are *gaining* thousands of pieces of immortal, infinitely toxic e-waste.
So there's that.
Then there's this: Jason Koebler just published a breakdown of a leaked sSamsung repair contract on 404 Media, revealing how Samsung requires its "independent" repair partners to trick you, abuse you, spy on you, and literally destroy your phone:
First: every time you bring a phone to an independent Samsung repair shop, the company has 24 hours to notify Samsung, providing your name, email, phone number, address, the IMEI of your phone, your warranty status and complaint.
Then, the technician is required to inspect your device for any evidence that you have had it serviced by unauthorized technicians or fixed with third-party replacement parts. If they believe you have failed to act in accord with Samsung's shareholders' interests, the technician is required to *immediately destroy your phone* and notify Samsung.
(This is radioactively illegal, and has been since 1975, when Congress passed the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act, which protects your right to use third-party parts:)
Why does Samsung do this? They can't help themselves. It's in their nature.
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
strips AI out of Google search results, giving you just the pages
more info ⬇️
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Another option for deleting AI from your search results.
#remember when Google's mottoes were ''Don't Be Evil'' and ''Remember the Human''?#those were the days
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
How America's oligarchs lull us with the be-your-own-boss fairy tale

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/16/narrative-capitalism/#sell-job

Capitalism is a vibes-based system. Sure, we all know about Keynes's "Animal Spirits" that see "bulls" and "bears" vying to set the market's future, but beyond that, there's just a hell of a lot of narrative.
Writing for The American Prospect, Adam M Lowenstein reviews two books that tell the histories of the stories that are used to sell American capitalism to the American people – the stories that turn workers into "temporarily embarrassed millionaires":
https://prospect.org/culture/books/2024-02-16-stories-corporations-tell-williams-waterhouse-review/
The first of these books is Taming the Octopus: The Long Battle for the Soul of the Corporation, by Kyle Edward Williams, a kind of pre-history of "woke capitalism":
https://wwnorton.com/books/9780393867237
Taming is a history of the low-water marks for Big Business's reputation in America, and how each was overcome through PR campaigns that declared a turning point in which business leaders would pursue the common good, even at the expense of their shareholders' interests.
The story starts in the 1950s, when DuPont and other massive firms had gained a well-deserved reputation as rapacious profit-generation machines that "alienated workers and pushed around small businessmen, investors, and consumers." This prompted DuPont's PR chief, Harold Brayman, to write a memo called "The Attack on Bigness," where he set out a plan to sell America on a new cuddly image for corporate giants.
For Brayman, the problem was that corporate execs were too shy about telling their social inferiors about all the good that businesses did for them: "The businessman is normally reluctant to talk out loud. He frequently shuns the spotlight and is content with plugging his wares, not himself."
This was the starting gun for a charm offensive by American big business that included IBM president Thomas Watson Jr ("I think there is a world market for about five computers") going on a speaking tour organized by McKinsey & Co, where he told audiences that his company's billion dollar annual profits had convinced it to assume "responsibilities for the broader public welfare."
This set the template for a nationwide mania of "business statesmanship" that Fortune celebrated with an editorial announcing "a great transformation, of which the world as a whole is as yet unaware" that put the "profit motive…on its last leg."
Fortune then spent the next seventy years recycling this announcement, every time the tide went out on business's popularity. In 2019, Fortune platformed IBM president Ginni Rometty for an announcement that the company was orienting its priorities to the public good: "It’s a question of whether society trusts you or not. We need society to accept what it is that we do."
The occasion for Rometty's quote was a special package on the Trump tax-cuts, a trillion-dollar gift to American big business, which lobbyists for the Business Roundtable celebrated with an announcement that American capitalism would now serve "stakeholders" (not just shareholders). Fortune celebrated this "change" as "fundamental and profound."
Fast forward five years and corporate leaders are still telling stories, this time about "stakeholder capitalism" and "ESG" – the dread "woke capitalism" that has right-wing swivel-eyed loons running around, hair afire, declaring the end of capitalism.
For Williams and Lowenstein (and me), all this ESG, DEI, and responsible capitalism is just window dressing, a distraction to keep the pitchforks and torches in people's closets, and to keep the guillotines in their packaging. The right-wing is doing a mirror-world version of liberals who freak out when OpenAI claims to have built a machine that will pauperize every worker – assuming that a PR pitch is the gospel truth, and then repeating it in criticism. Criti-hype, in other words:
https://sts-news.medium.com/youre-doing-it-wrong-notes-on-criticism-and-technology-hype-18b08b4307e5
Think of ESG: the right is freaking out that ESG is harming shareholders by leaving hydrocarbons in the ground to appease climate-addled greenies. The reality is that ESG is barely disguised greenwashing, and it's fully compatible with burning every critter that died in the Mesozoic, Cenozoic, and lo, even the Paleozoic:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/03/15/sanctions-financing/#profiteers
The reason this tactic is so successful is that Americans have also been sold another narrative: that American problems are solved by American individuals as entrepreneurs and businesspeople, not as polities or as members of a union (let alone the working class!).
This is the subject of the second book Lowenstein reviews, One Day I’ll Work for Myself: The Dream and Delusion That Conquered America, by Benjamin Waterhouse:
https://wwnorton.com/books/one-day-ill-work-for-myself/
A keystone of American narrative capitalism is the idea that the USA is a nation of small businesspeople, Jeffersonian yeoman farmsteaders of the US economy. But even a cursory examination shows that the country is ruled – economically and politically – by very large firms.
Uber sells itself as a way to be your own boss ("No shifts. No boss. No limits.") – even though it's a system where the app is your boss, and thanks to that layer of misdirection, Uber gets to be the worst conceivable boss, while its workers have no recourse in labor law:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
In labor fights, Uber represents itself as the champion of innumerable "small businesspeople" who drive its unlicensed taxis. In consumer protection fights, Amazon claims to be fighting for "small businesspeople" who sell on its platform. In privacy fights, Facebook claims to represent "small businesspeople" who buy its surveillance advertising.
But large firms are actively hostile to small firms, seeing them as small-fry to be rooked or destroyed (recall that when Amazon targeted small publishers for bankruptcy-level discounts, they called the program "The Gazelle Project" and Bezos told his executives to tackle these firms "the way a cheetah pursues a sickly gazelle").
Decades of this tale have produced "a profound shift from a shared belief that individuals might come together to solve problems, into a collective faith in individual effort." America's long love-affair with rugged individualism was weaponized in the 1970s by corporations seeking to shed their regulatory obligation to workers, customers, and the environment.
As with Big Tech today, the big business lobby held up mom-and-pop businesses as the true beneficiaries of deregulation, even as they knifed these firms. A telling anecdote comes from someone who worked for the Chamber of Commerce's magazine Nation's Business: when this editor pointed out that many of the magazine's subscribers were small businesspeople and asked if they could start including articles relevant to mom-and-pops, the editor in chief said, "Over my dead body."
The neoliberal era has been an unbroken string of platitudes celebrating the small business and policies that annihilate their chances against large firms. Ronald Reagan's dewy-eyed hymns to American entrepreneurship sounded nice, but what matters is that he attempted to abolish the Small Business Administration and refused to address the 20,000 attendee "White House Conference on Small Business."
In the years since, American has sacrificed its small businesses while pulling out all the stops – bailouts and tax cuts and elite bankruptcy – to keep its largest firms growing. New regulations like Dodd-Frank were neutered in the name of saving mom-and-pop shops, even though the provisions that were cut already exempted small businesses.
Today, millions of Americans are treading water in a fetid stew of LLC-poisoning, rise-and-grind, multi-level-marketing, dropshipping and gig-work, convinced that the only way to get a better life is to pull themselves up by their bootstraps:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/10/declaration-of-interdependence/
Narrative does a lot of work here. The American economy runs on bubbles, another form of narrative capitalism. Take AI, a subject I sincerely wish I could stop hearing about, not least because I'm certain that 99% of that thinking is being wasted on whatever residue remains after the bubble pops:
https://locusmag.com/2023/12/commentary-cory-doctorow-what-kind-of-bubble-is-ai/
AI isn't going to do your job, but its narrative may convince your boss to fire you and replace you with a bot that can't do your job. Like what happened when Air Canada hired a chatbot to answer customer inquiries and it started making shit up about bereavement discounts that the company later claimed it didn't have to honor:
https://bc.ctvnews.ca/air-canada-s-chatbot-gave-a-b-c-man-the-wrong-information-now-the-airline-has-to-pay-for-the-mistake-1.6769454
This story's been all over the news for the past couple of days, but so far as I've seen, no one has pointed out the seemingly obvious inference that this chatbot probably ripped off lots of people. The victim here was extraordinarily persistent, chasing a refund for 10 weeks and then going to the regulator. This guy is a six-sigma self-advocate – which implies a whole bell-curve's worth of comparatively normal people who just ate the shit-sandwich Air Canada fed them.
The reason AI is a winning proposition for Air Canada isn't that it can do a customer service rep's job – it can't. But the AI is a layer of indirection – like the app that is the true boss of Uber drivers – that lets Air Canada demoralize the customers it steals from into walking away from their losses.
Nevertheless, the narrative that AI Will Change Everything Forever is powerful – more powerful than AI itself, that's for sure. Take this Bloomberg headline: "Nearly all wealth gained by world's rich this year comes from AI":
https://www.business-standard.com/world-news/nearly-all-wealth-gained-by-world-s-rich-this-year-comes-from-ai-124021600006_1.html
Dig in and you find even more narrative. The single largest beneficiary of AI stock gains last year was Mark Zuckerberg ($161B!). Zuck is American Narrative Capitalism's greatest practitioner: the guy who made billions peddling a series of lies, from "pivot to video" to "metaverse," leaping from one lie to the next just ahead of the mass stock-selloffs that wiped out lesser predators.
The Narrative Capitalism Cinematic Universe has a lot of side-plots like AI and entrepreneurship and woke capitalism, but its main narrative arc was articulated, ad nauseum, by Margaret Thatcher: "There is no alternative." This is the most important part of the story, the part that says it literally can't be otherwise. The only way to organize society is through markets, and the only way to organize markets is to leave them alone, no matter how much suffering they cause.
This is a baffling story, because it's so easily disproved. Zuck says the only way to have friends is to let him surveil you from asshole to appetite, even though he once ran Facebook as the privacy-forward alternative to MySpace, and promised never to spy on you:
https://lawcat.berkeley.edu/record/1128876
Likewise, the business leaders – and their chorus of dutiful Renfields – who insist that monopoly is the natural and inevitable outcome of any market economy just handwave away the decades during which anti-monopoly enforcement actually kept most businesses from getting too big to fail and too big to jail.
I'm no champion of market efficiency – especially not as the best and final arbiter of social and economic questions – but when I hear my comrades repeating the Thatcherite claims that all forms of capitalism necessarily degrade into monopolistic quagmires, that there is no alternative, it sounds like more criti-hype.
This is a frequent point of departure during discussions of enshittification: some people dismiss the whole idea of enshittification as "just capitalism." But we had decades of digital services that either didn't degrade, or, when they did, were replaced by superior competitors with a minimum of switching costs for users who migrated from the decaying incumbent to greener pastures.
The reality is that while there are problems with all forms of capitalism, there are different kinds of capitalist problems, and some forms of capitalism are less harmful to working people and more capable of enacting and enforcing sound policy than others.
Enshittification is what happens when the constraints on the worst impulses of companies and their investors and managers are removed. When a company doesn't have competitors, when it can capture its regulators to trample our rights with impunity, when it can enlist those regulators to shut down would-be competitors who might free us from its "walled garden," and when it can fire any worker who refuses to enact harm upon the users they serve, then that company will enshittify:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/30/go-nuts-meine-kerle/#ich-bin-ein-bratapfel
A company can be made to treat you well, even if it is run by a wicked person who sees you as a mark to be fleeced – that mustache twirler just has to be constrained – by competition, regulation, self-help and labor. He may still hate you and wish you harm, but he won't be able to act on it.
As MLK said:
It may be true that the law cannot make a man love me, religion and education will have to do that, but it can restrain him from lynching me. And I think that's pretty important also. And so that while legislation may not change the hearts of men, it does change the habits of men. And we see this every day.
#pluralistic#narrative capitalism#oligarchy#temporarily embarrassed millionaires#late-stage capitalism#enshittification#disenshittification#vocational awe#fobazi ettarh#ai#bubbles#bubblenomics#rise and grind#Benjamin C. Waterhouse#One Day I’ll Work for Myself#Kyle Edward Williams#Taming the Octopus#woke capitalism#llcs with mfas
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
To those worried about Google, the one place where its own search engine is being replaced by ay-eye generated features (no thanks to those ASMR elitists out there who wanna milk it till it explodes), I discovered a newly introduced backup.
It's &udm14. As the quote emplies, it's a quick way to get an ay-eye-free search without any extra work. Just click on the bar, type whatever you'd like, click ay-eye-free search, and that's it! No need to load up your own account or see something horrific. You'll thank me later.
Or, maybe not.
0 notes
Text
you know that code folks discovered to clean up google searches? someone made a website for it!
0 notes
Text
&udm=14 – the disenshittification Konami code
https://udm14.com/
1 note
·
View note
Text
End to End

In “End to End,” my new column for Locus Magazine, I propose a policy framework for a better internet: the “End to End” principle (E2E), a bedrock of the original design for the internet, updated for the modern, monopolized web, as a way of disenshittifying it:
https://locusmag.com/2023/03/commentary-cory-doctorow-end-to-end/
If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/07/disenshittification/#e2e
The original E2E marked the turning point from telco-based systems where power was gathered at the center, controlled by carriers, to the packet-switched internet, where power moved to the edges. Under the old model, only the network operator could add new features. If you wanted to create, say, Caller ID, you needed to convince the phone company to update its switches to support a new signaling system (and you probably had to rent a Caller ID box from the carrier, too).
But packet-switching made it possible for new services to be created by people at the edges of the network. Once your device was connected to the internet, it could exchange data with any other device on the internet. If someone set up a voice-calling system and you connected to it, they could add Caller ID to it without asking Ma Bell for permission.
End to end was the core ethic of this system: the idea that the telcos that sat beneath these systems should get out of the way of their users, serving only to deliver data from willing senders to willing receivers as quickly, efficiently and reliably as possible.
E2E was a powerful idea, one that truly treated the telcos as utilities — the plumbing that sat beneath the services, obliged to serve its subscribers by doing their bidding to the extent they could. If you chose to use a internet calling service instead of making phone calls, the carrier’s job was to shuttle those packets around, not to slow them down or block them to funnel you into its rival service.
There’s a powerful logic to this: no one rents a phone line because they want to make sure that the carrier’s shareholders are getting the highest possible return on their investment. The reason we buy network connections is to get to the services we value.
We have no duty to arrange our affairs to the benefit of a carrier’s shareholders. If those shareholders are so emotionally fragile that they can’t bear the thought of network users making their own choices on which services to use, they should get into a different line of work.
E2E wasn’t a law, it was a principle. Principles are useful! They can be embedded in laws (for example, the laws that establish most network providers as common carriers often include an E2E rule), but just as importantly, they can give us a vocabulary for critiquing or designing services: “Ugh, I won’t use that service, it’s not end to end,” or “How can we make this work in an end to end way?”
Principles can be integrated into professional codes of ethics, or procurement rules for public bodies (“Our university only buys end to end services”). Tech groups and publications can use principles to rank competing technologies (“Which network providers are end to end?”).
Network Neutrality is a way of operationalizing E2E: the idea of Net Neutrality is that carriers should be obliged to treat all traffic the same. If you request Youtube packets from Comcast, Comcast should deliver those packets as quickly and reliably as it can, even though its parent company, Universal, owns several competing services.
Net Neutrality can be treated as a principle (“This ISP sucks — it violates Net Neutrality”) or as a regulation (“The FCC is fining your ISP because it violated Net Neutrality”). As a regulation, Net Neutrality has a problem: it’s hard to administer, because it’s very difficult to detect Net Neutrality violations. The internet is a “best effort” network, with no service guarantees, so when your Youtube connection starts to jitter, it’s hard to prove that this is because Comcast is screwing with it, as opposed to regular network congestion.
Which brings me to my E2E proposal: end to end for services. Contemporary services have no E2E. If you search for a product on Amazon, Amazon often won’t show you that product until you’ve looked at five screens’ worth of other products that have paid Amazon to interrupt your search:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
If you hoist an email out of Gmail’s spam folder and add the sender to your address book, Gmail will still send that message to spam, or even block its server. It’s incredible that we had a Congressional debate about whether Gmail should mark politicians unsolicited fundraising emails as spam but not whether emails from your reps that you asked to receive should be delivered:
https://doctorow.medium.com/dead-letters-73924aa19f9d
Platform creators are workers whose boss is an algorithm that docks every paycheck to punish them for breaking rules they aren’t allowed to know about, because if the boss told you the rules, you’d learn how to violate them without him being able to punish you for it. Again, it’s wild that we’re arguing about “shadowbanning” (a service choosing not to send your work to people who never asked to see it), while ignoring the fact that platforms won’t deliver your posts to people who explicitly subscribed to your feed:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys
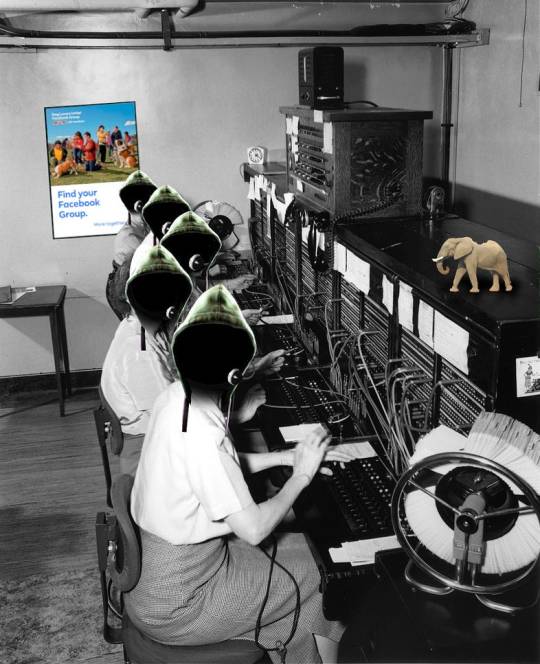
Alexander Graham Bell’s first telephone operators were young boys who entertained themselves by deliberately misconnecting calls, putting you in contact with people you never asked to talk to and refusing to connect you with the people you were trying to converse with.
As @brucesterling wrote in The Hacker Crackdown:
The boys were openly rude to customers. They talked back to subscribers, saucing off, uttering facetious remarks, and generally giving lip. The rascals took Saint Patrick’s Day off without permission. And worst of all they played clever tricks with the switchboard plugs: disconnecting calls, crossing lines so that customers found themselves talking to strangers, and so forth.
https://www.mit.edu/hacker/hacker.html
Bell fired those kids. Even the original telecoms monopolist understood that the point of a telephone network was to connect willing speakers with willing listeners.
Today’s tech barons are much more interested in charging other people to interrupt your consensual communications with nonconsensual and often irrelevant nonsense and ads. This is part of the enshittification cycle: first, the platforms lock you in by giving you a good deal, including feeds that contain the things you ask to see and search boxes that return the thing you’re looking for.
Then, platforms take away your surplus and give it to business customers. They spy on you and use the data to help target you on behalf of advertisers, whom they charge low rates for ads that are reliably delivered. They insert performers’ and media companies’ posts into your feed, generating traffic funnels that result in clicks to off-platform sites. They offer low fees and even subsidies to platform sellers and creators who produce DRM media, like ebooks and audiobooks.
Users get locked into the platform — by the collective action problem of convincing their friends to leave, by the collapse of local retail that can’t match the investor-funded subsidies of would-be monopolists, by DRM that they are legally prohibited from removing, causing them to lose their investment if they quit the service.
Business customers also get locked to the platform: platform sellers have to sell where the buyers are; publishers and creators have to provide media where the audiences are; advertisers have to run ads on the services they’ve optimized for.
Once everyone is locked in, the platform can fully enshittify, harvesting surpluses from users and business customers for themselves. Platforms can hike fees, charge media companies and creators to reach their own subscribers, block posts with links off-site, insert ads into media (like Audible is doing with paid audiobooks!), and so on.
This is the cycle that E2E seeks to interrupt. E2E for services would dictate that platforms should connect willing speakers and willing listeners. The best match for your search should be at the top of the results — even if someone is willing to pay more to put a worse match there. Emails should be delivered to people you’ve told your provider you want to correspond with — not sent to a spam folder or blocked.
As with the original E2E, there’s lots of ways we can use this principle. It can simply be a term for criticizing platforms (“You aren’t sending my posts to the people who follow me — that’s a violation of the end to end principle!”). It can be a law (“It is a deceptive and unfair practice for ecommerce companies to deliberately return search results that are not the best match they can locate for the users’ query”). It can be a punishment (“The FTC settled with Google today and ordered the company to implement a Gmail feature that permits users to identify senders whose messages will never be blocked or sent to spam”).
Lots of people are pissed off about Big Tech and many have proposed that we could make it better by treating platforms as “utilities.” But I don’t want President DeSantis to run my email provider, or to decide what’s too “woke” for me to see (or post) on social media.
An E2E rule, on the other hand, creates a role for government that doesn’t determine who gets to speak or what they get to say — rather, it ensures that when people speak and to others who want to hear them, the message gets through.
Unlike Net Neutrality, E2E is easy to administer. If I claim that your emails are being sent to spam after I marked you as a sender I want to hear from, we don’t have to do a forensic investigation into Google’s mail servers to determine if I’m right. You just send me an email we observe where it lands.
Likewise for search: if I search Amazon for a specific product or model number, it’s easy to tell whether that product is at the top of the search results or not.
Same goes for delivery to subscribers: if we suspect that Twitter is shadowbanning posters — say, for including their Mastodon addresses in their bios, or linking to posts on Mastodon — we just send some test messages and see whether they are delivered.
Beyond administratability, E2E has another advantage: cheap compliance. Lots of the rules we’ve created or proposed for service providers are incredibly complex and expensive to comply with. Take rules about “lawful but awful” content, which require platforms to somehow determine whether a message constitutes harassment and block it if it does.
These rules require an army of expensive human moderators or a vast, expensive machine learning system, or both — so they guarantee that Big Tech will rule the internet forever, because no one else can afford to launch a new service with better community norms and better practices.
By contrast, E2E is cheap to comply with. Trusted-sender lists for email providers, search engines that put best results first, and content delivery algorithms that show you the things you asked to see in the order that they were posted are all solved problems:
https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2023/03/social-media-algorithms-twitter-meta-rss-reader/673282

This isn’t to say that platforms wouldn’t be allowed to offer algorithmic feeds and results. Think of how Tumblr does it: you can choose between a feed called “Following” (posts from people you follow) or “For You” (posts that Tumblr thinks you’ll enjoy). Forcing platforms to clearly label their recommendations and give you the choice of controlling your own feed is a powerful check against enshittification.
If you know when you’re in charge and when the platform is driving things, and if you can toggle away from platform-determined feeds to ones that you design, the platform has to be better than you at choosing what you see, or you won’t choose its recommendations.
Platform owners have hijacked the idea that “freedom of speech isn’t freedom of reach” to justify the now-ubiquitous practice of overriding users’ decisions about what they want to see:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
The Old Internet had lots to going for it. It wasn’t perfect, though. While it was easy to find the things you knew you liked, it could be hard to find things you didn’t know you liked. Recommendations, whether they come from an algorithm or a human editor, are a source of endless delights. But when a we find something we like through one of those recommendations, we need to know that we can find more from that source if we choose to.
Sometimes it’s nice to scroll an algorithmic feed and get a string of surprises. But we are forced to use those feeds, they will inevitably enshittify, to our detriment, and to the detriment of the people who make the things that please us.
As ever, the important thing about a technology isn’t what it does, it’s who it does it for and who it does it to. When we control our feeds, we can choose to let a recommender system do the driving. If we’re locked into a recommendation system, it drives us.
Today (Mar 7), I’m doing a remote talk for TU Wien.
On Mar 9, you can catch me in person in Austin at the UT School of Design and Creative Technologies, and remotely at U Manitoba’s Ethics of Emerging Tech Lecture.
On Mar 10, Rebecca Giblin and I kick off the SXSW reading series.
Image:
Felix Andrews (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Elephant_side-view_Kruger.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
[Image ID: A room full of telephone operators at a switchboard; their heads have been replaced with hacker-in-a-hoodie heads. On the wall behind them is a poster ad for Facebook with the slogan, 'Find Your Facebook Group.' Atop the switchboard stands a small elephant with a bite taken out of its back.]
#pluralistic#enshittification#disenshittification#e2e#end to end#feeds#algorithmic feeds#search#reverse chrono#rss#amazon#net neutrality
105 notes
·
View notes
