#fashion history
Text
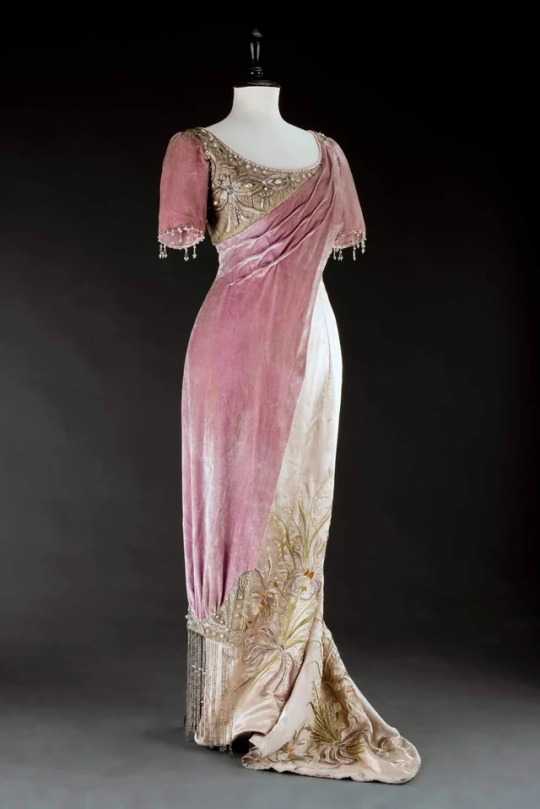

Evening Gown
c. 1908
Museum of Arts and Crafts, Prague
#Edwardian#art nouveau#edwardian gown#edwardian fashion#dress history#historical fashion#fashion history#1900s#1900s fashion#frostedmagnolias
116 notes
·
View notes
Text
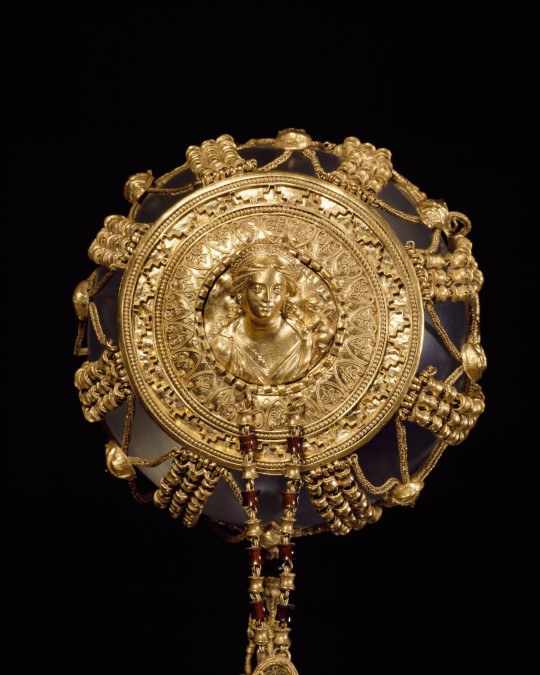
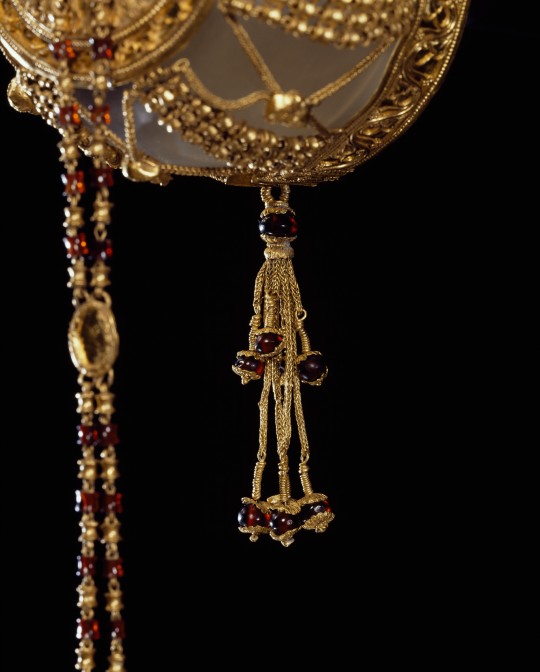
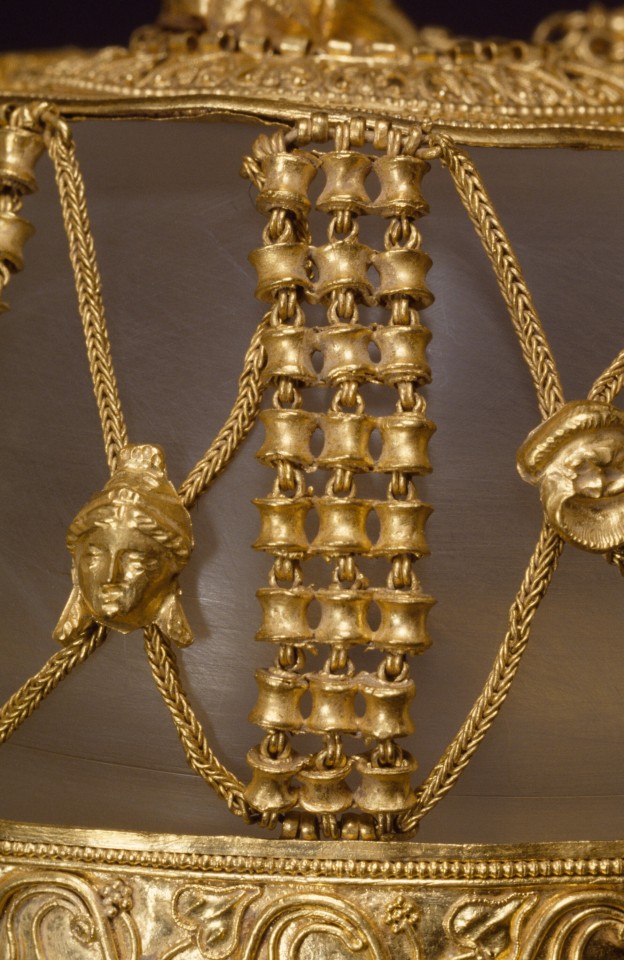




Gold hairnet, Ptolemaic, 225-175 BCE
From the Getty Villa Museum
#hairnet#gold#fashion#fashion history#accessory#history#225 bce#200s bce#175 bce#100s bce#bce#ancient#ptolemaic#ancient greek#ancient egyptian#greek#egyptian#ancient greece#ancient egypt
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
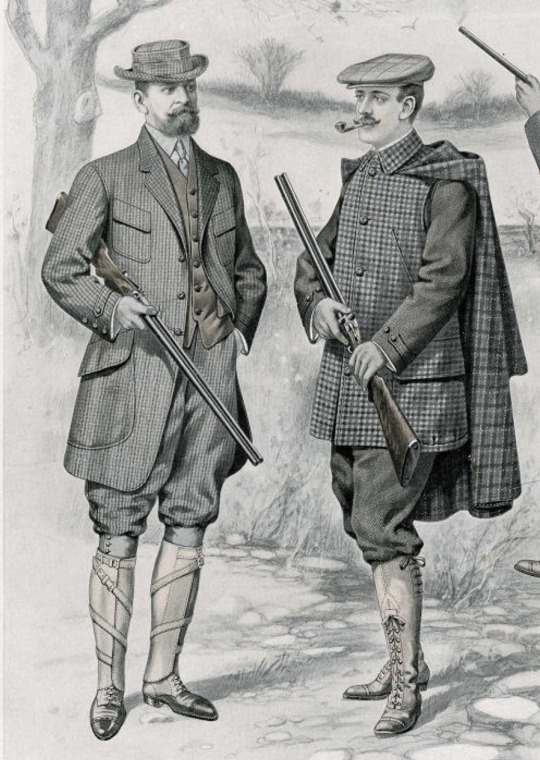

#the BOOTS 😍#historical fashion polls#fashion poll#historical dress#historical fashion#dress history#fashion history#fashion plate#20th century fashion#early 20th century#20th century#1900s style#1900s dress#1900s fashion#circa 1900#early 1900s#1900s#1906#tw gun
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
#chernobyl#allie haze#bnha imagines#70s#nico di angelo#larry stylinson#stick and poke#avatar the last airbender#supercar#mammon#fashion history#pitch perfect#trans is beautiful#90's
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
another one

also they had popular non-arsenical green dyes in every period where arsenic/Scheele's Green was used
I guess you could intentionally sweat in a garment and see if it gives you a rash? but I wouldn't like Recommend that and you'd have to control for allergens and such
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
#hippies#punkflower#alysha nett#avatar the last airbender#miss you#supercar#mammon#fashion history#ldr#suzy#trans is beautiful#california#kakashi x reader#omori#choni
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
Robe à la Française, Part II
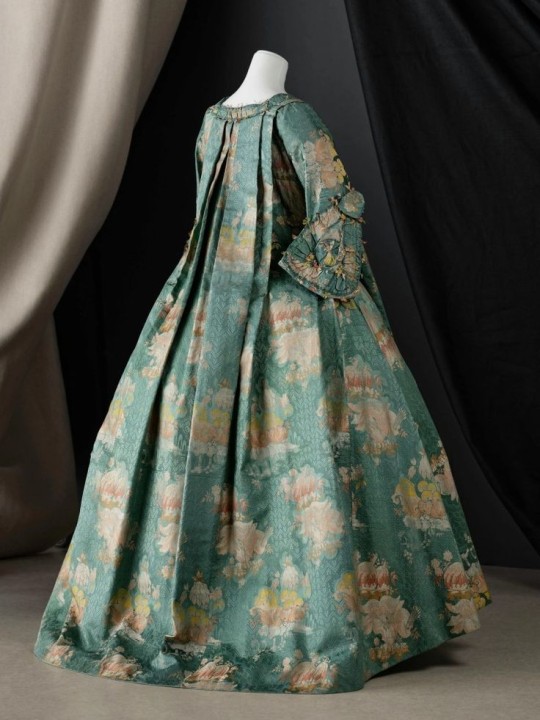

Fig. 1: Robe à la française • 1730-1740 • © Stanislas Wolff / Paris Musées, Palais Galliera
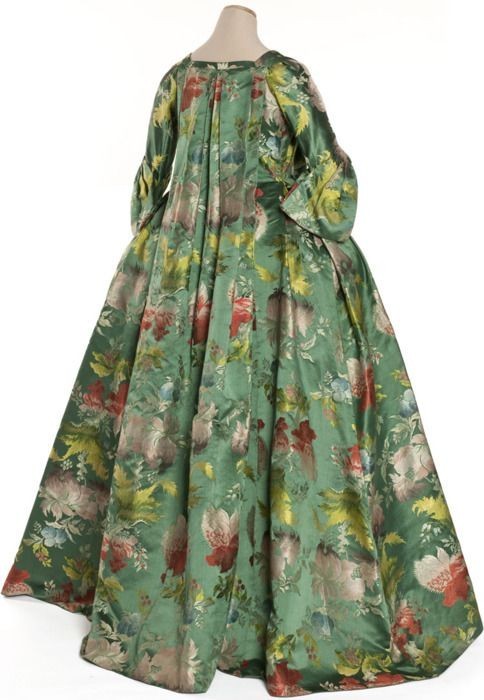
When I was researching the Rococo fashion era, I collected so many images and I have to share some of my favorites. It's not so much the style of the Robe à la Française that I like (though I do very much like the box pleats and drape of the back) but the fabrics, colors, and patterns. Fig. 1 shows a gorgeous print in a beautiful color combination. Such a print for a dress today wouldn't work very well, as contemporary dresses don't have the volume of the 18th century styles, nor the lovely draping in the back of the Robe à la Française.
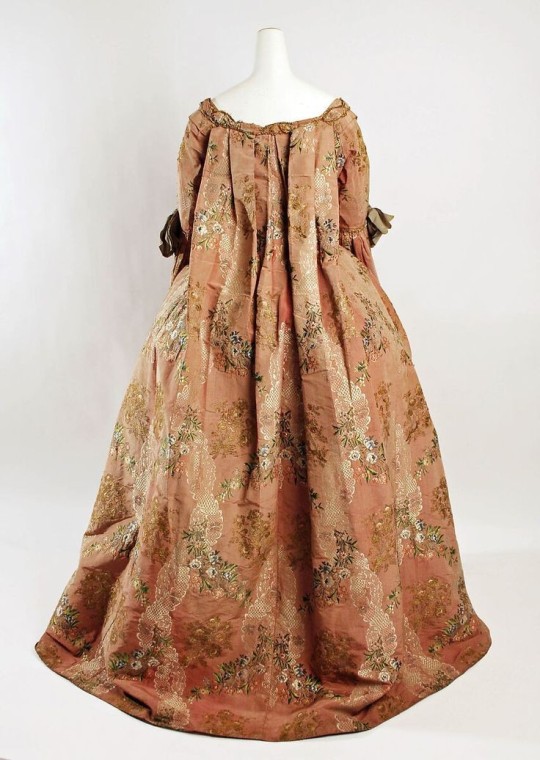
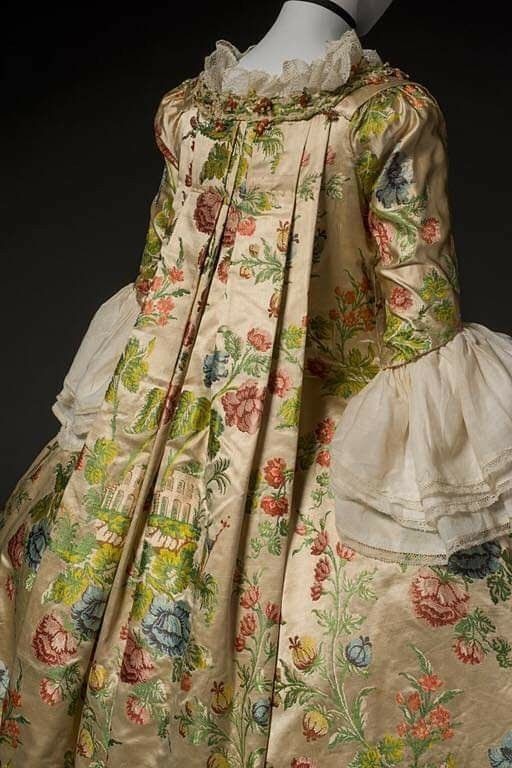


The Robe à la Française was derived from the loose negligee sacque dress of the earlier part of the century, which was pleated from the shoulders at the front at the back.
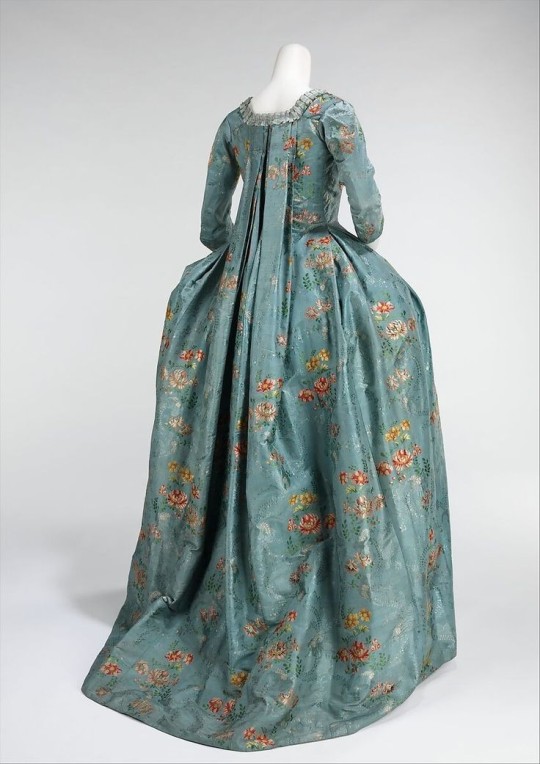
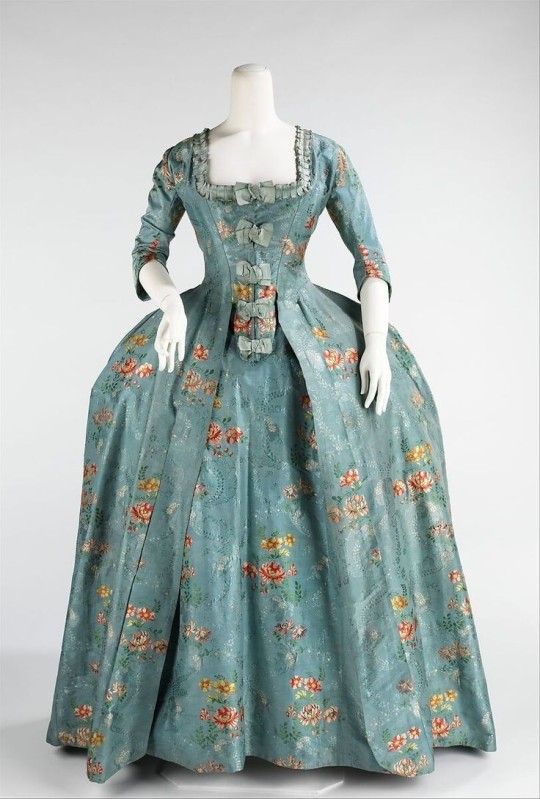


Metropolitan Museum of Art • 1760-70 • Silk, cotton
The silhouette was achieved with a funnel-shaped bust joining wide rectangular skirts. The wide skirts were supported by panniers and hoops constructed from cane, metal, and baleen. Fig. 2 shows a portrait sitter wearing a Robe à la Française with a contrasting underskirt.
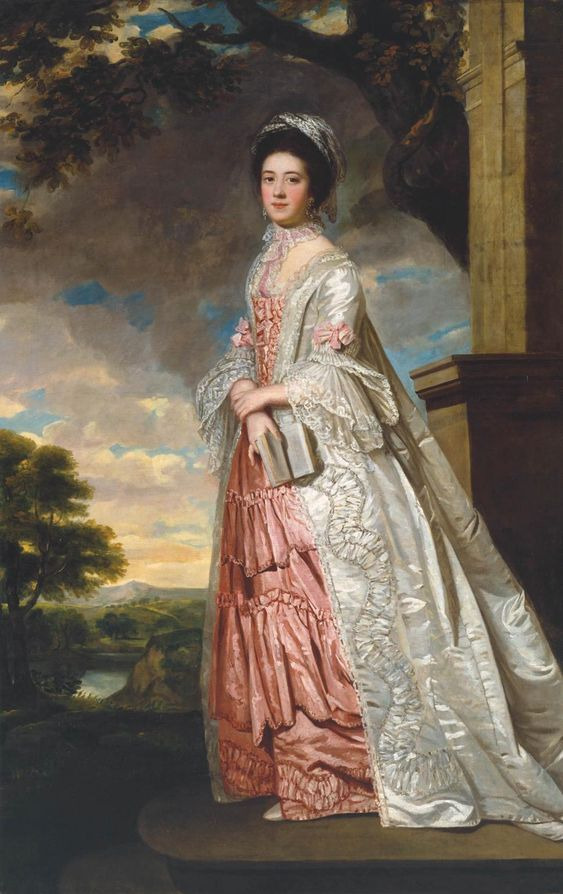

Fig. 2: Artist unknown (British). Mrs. Cadoux, ca. 1770
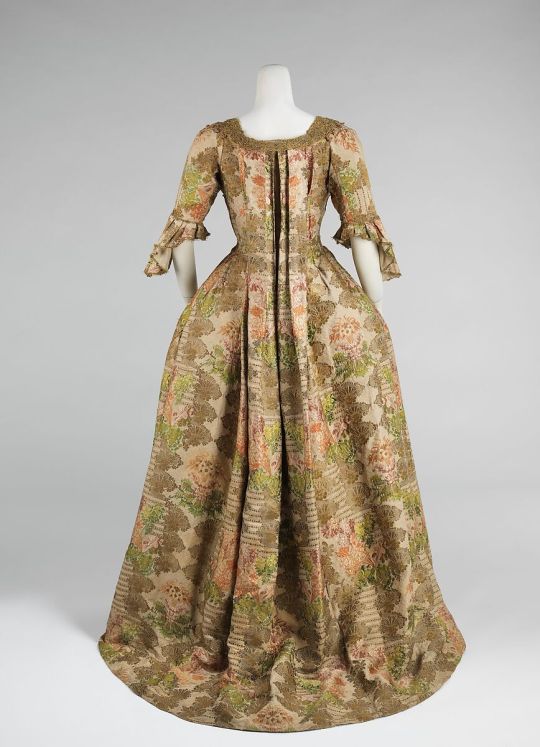


#art#portrait#fashion history#georgian fashion#rococo era fashion#robe à la française#1700s fashion#women's fashion history#18th century dresses#the resplendent outfit blog#sacque dress#metropolitan museum of art fashion Institute#textile patterns#fashion blogs on tumblr
30 notes
·
View notes
Note
This is maybe a dumb question, but looking at the portraits of Hervey, I have a hard time noticing anything about how he's dressing that seems out of the ordinary or especially more 'feminine' for the time period (barring that one where he just has his coat buttoned super low and his whole shirt out?). Am I missing some obvious detail (material they were made out of maybe?) or was the his effeminacy/the perception of him as effeminate just more based on behavior than 'presentation'?
Not a dumb question at all. It was combination of his sexuality, his diet, his androgyny as well as his clothes & makeup. While Hervey's femininity was almost certainly exaggerated in satire written by his enemies there was some basis to this satire.
Sexuality
In the 18th century there was an association between effeminacy and sodomy. I don't think we can discount the role the rumours surrounding Hervey's sexuality played in the public's perception of him. William Pulteney's 1731 pamphlet A Proper Reply to a Late Scurrilous Libel satirises Hervey as Mr. Fainlove. Pulteney describes Fainlove as a "delicate Hermophrodite", a "pretty, little, Master-Miss" and insinuates that he's a pathick who "enjoys every Moment and Fruits of his Guilt". The 1739 pamphlet The State of Rome, Under Nero and Domitian satirises Hervey as Sporus (an allusion to Pope's satire of Hervey) describing him as a "Male-female Thing," who is "Fit only for the Pathicks loathsome Trade".
Pope's choice to satirise Hervey as Sporus in An Epistle from Mr. Pope, to Dr. Arbuthnot (1735) was itself a comment on Hervey's sexuality. Sporus being the boy that Nero is said to have castrated and taken as a wife.
Diet
Hervey was epileptic and suffered from a chronic colic. He details his medical history in An Account of My Own Constitution and Illness. At the recommendation of his doctor's George Cheyne he adopted a milk and vegetable diet. Cheyne believed that such a diet was "absolutely necessary for the total Cure of the Epilepsy” and also prescribed milk and vegetable diets in cases of “extreme Nervous Cholicts”. (The English Malady, p167 & 254) Hervey ate no meet for three years before reintroducing white meet. This diet was seen as effeminate by his contemporaries. Lady Louisa Stuart cites his refusal to eat beef as an example of the “extreme to which Lord Hervey carried his effeminate nicety”. (Stuart wrote this anonymously in the introductory anecdotes included in the 1837 edition of The Letters and Works of Lady Mary Wortley Montagu.)
Hervey also drank "ass’s milk with powder of crab’s eyes and oyster-shells" for his heath. This is mocked in the poem The Lord H-r--y's First Speech in the House of Lords (1733-4) that calls him "a perfect curd of ass's milk." Alexander Pope included a similar line in An Epistle from Mr. Pope, to Dr. Arbuthnot (1735) describing him as a "mere white Curd of Ass's milk".
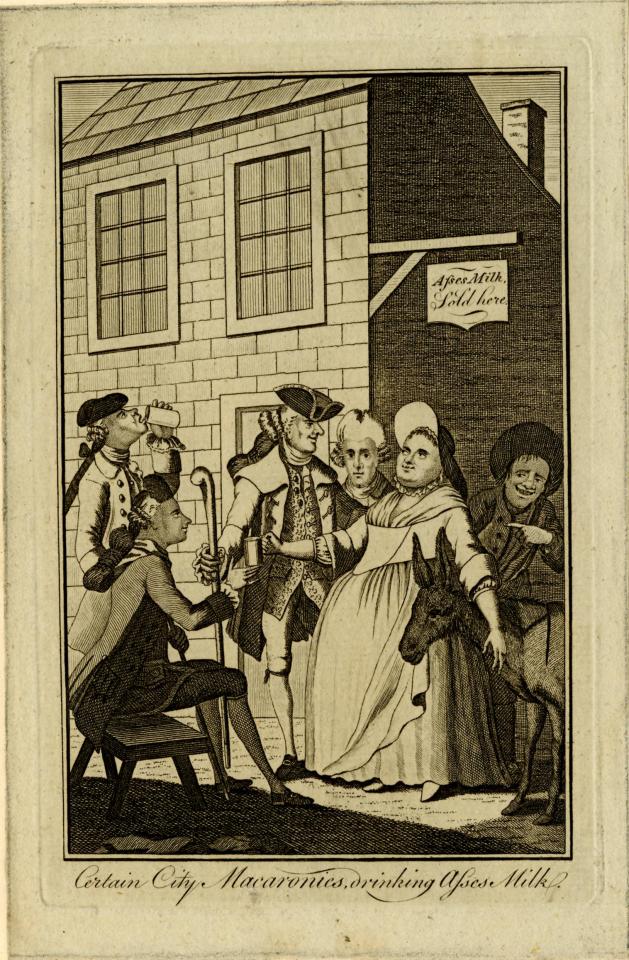

[Certain City Macaronies drinking Asses Milk, print, c.1772, via The British Museum.]
The association between effeminacy and asses milk features in the satirical dialogue The City Macaronies drinking Asses-milk, at the Lacteum, in St. George's-fields published in the November 1772 edition of the Oxford Magazine which was accompanied by the above illustration. The dialogue mocks macaroni for drinking asses-milk as a treatment for "nervous cases" and "hysterics" claiming that it's "delicate men" such as the macaroni "whose fine feelings are sensible of the slightest pressure, that are acquainted with hysterics". The son of the milk woman wonders aloud whether the macaroni are men or women. His mother tells him "they're neither, they are a kind of half and half breed."
Androgyny
With his slim figure and a bit of a baby-face Hervey was considered to be naturally androgynous. When Lady Deloraine said to him and Miss Fitzwilliams that "in her opinion a woman could never look too much like a woman, nor a man too much like a man" Hervey admitted that "considering the two people she said this to, it was certainly well said; and I can forgive her having bragged of it to every creature she has seen since" (Hervey to Stephen Fox, 18 September 1731)
Satirical descriptions of Hervey liken him to a cherub or a fairy describing him as pretty, little, soft, dainty, delicate.
In A Proper Reply to a Late Scurrilous Libel (1731) Pulteney satirises Hervey as "pretty Mr. Fainlove" who he describes as a "delicate Hermophrodite", a "pretty, little, Master-Miss", a "pretty, little Scribbler", and comments that he shouldn't "sully those pretty Fingers with Ink" that "a Fan would become them much better than a Pen."
The Lord H-r--y's First Speech in the House of Lords (1733-4) describes him as "the softest, prettiest thing". In An Epistle from Mr. Pope, to Dr. Arbuthnot (1735) Pope describes him as having a "cherub's face". Tell-tale Cupids (1735) satirises him as the "pretty baby fac'd Lord Dapper".*
In A Fairy Tale (1743) by Horace Walpole depicts Hervey as a literal fairy describing him as a "Dainty little Figure", "most delicately Fair and light" who "would have been vastly Pretty if it’s cherry-lips had ‘nclos’d any Teeth".
*quoted in Lord Hervey: Eighteenth-Century Courtier by Robert Halsband
Clothes & Makeup
Pope didn't describe Sporus as a "bug with gilded wings" and a "Fop at the toilet" because of Hervey's natural androgyny, clothing & makeup absolutely played a role in the public perception of him.
The Duchess of Marlborough described Hervey as a having "a painted face, and not a tooth in his head". Pope described him as "painted Child of Dirt that stinks and stings". And the The Court Garland refers to him as "Thou powder-puff, thou painted toy". (see The Opinions of Sarah Duchess-Dowager of Marlborough p42, An Epistle from Mr. Pope, to Dr. Arbuthnot & Lord Hervey: Eighteenth-Century Courtier by Robert Halsband p138)
The fashionable look of the period required pale clear skin, flushed red cheeks and dark eyebrows. While washes and creams were used to achieve clear pale skin, white cosmetic paint could also be used to lighten and smooth the skin. Rouge was used to give colour to the cheeks. Burnt cloves could be used to darken the eyebrows. While some of these cosmetics contained lead or mercury not all of them did.
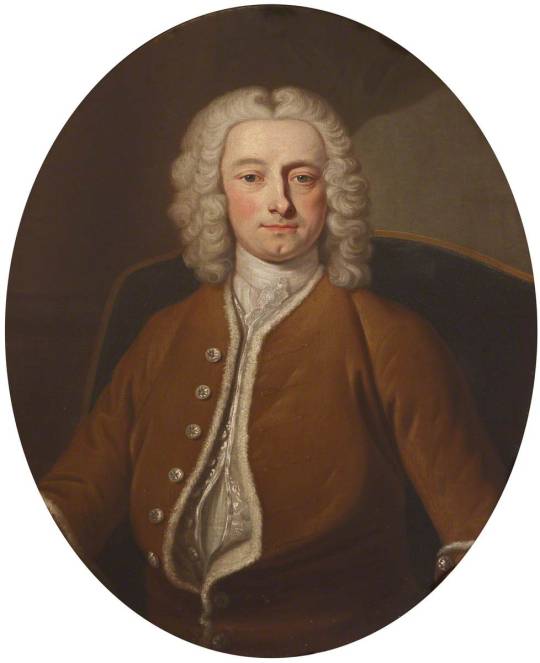

[Lord John Hervey, oil on canvas, c.1741–1742, by Jean-Baptiste van Loo, via Art UK.]
It's hard to know how reliable the accounts of Hervey's makeup use are however his portraits do depict him with this fashionable look (in particular the rosy cheeks of the Jean-Baptiste van Loo portraits and the Enoch Seeman portrait). While modern depictions of 18th century fops will sometimes exaggerate makeup depicting men with pure white faces and almost perfectly round red circles on their cheeks, Hervey's portraits are more accurate to the look these cosmetics were trying to achieve.
The use of cosmetics are highlighted in satirical depictions of effeminate men throughout the 18th century century. As early as 1691 Mundus Foppensis: or, the Fop Display’d was mocking men for the "wanton use" of "Spanish Red, and white Ceruse". In 1773 The Old Beau in an Extasy depicts a "Fop at Sixty two" who uses "Chinese Paint for Artificial Bloom". In 1812 Regency A la Mode depicts the Prince Regent applying rouge to his cheeks while he gets laced into stays. The Court Garland's satire of Hervey is just another example of a satirical depiction of a fop in makeup:
Thou powder-puff, thou painted toy,
Thou talking trifle, H----y;
Thou doubtful he, she, je ne sçai quoy,
By G-d, the K--g shall starve ye.
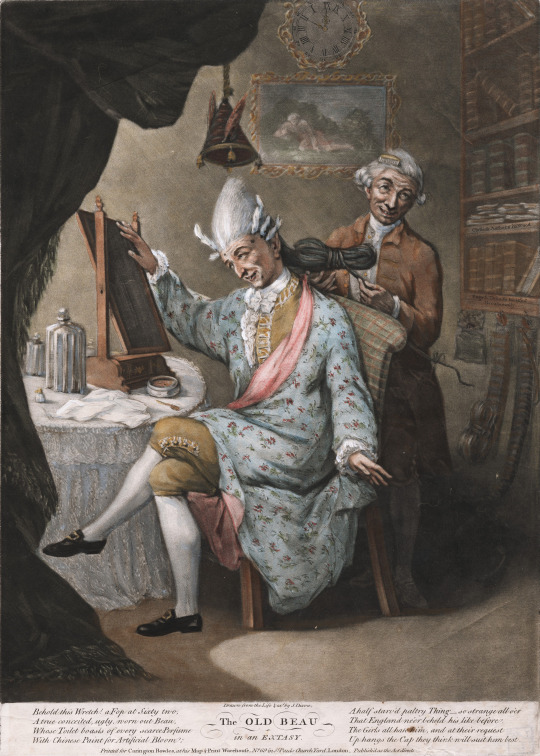


[Left: The Old Beau in an Extasy, print, c.1773, by John Dixon, via Lewis Walpole Library.
Right: 1812, or, Regency A la Mode, print, c.1812, by William Heath, via Lewis Walpole Library]
As for clothing I have to admit I'm better at late-18th century menswear. That being said material and colour seem to have played a role in what was considered effeminate.
A letter to the Read's Weekly Journal or British Gazetteer published on the 8th of May 1731 complains; "Rich and coloured Silks are in themselves effeminate, and unbecoming a Man; as are in short, all Things that discover Dress to have been his Study- 'Tis in vain for a Fop of Quality, to think his Title will protect him." In particular the article criticises poke sleeves and green waistcoats. While poke sleeves are absent from Hervey's portraits the Seeman portrait depicts him wearing a green waistcoat.
Green waistcoats are also mentioned in a story published in the Universal Spectator and Weekly Journal on the 18th of October 1729 describing and effeminate man's clothing as follows:
He had a flower’d pink-colour Silk Coat, with a Green-Sattin Waistcoat lac’d with Silver. Velvet Breeches, Clock’d Stockings the Colour of his Coat, Red-heel’d Pumps, a Blue Ribbon at the Collar of his Shirt, and his Sword-Hilt he embrac’d under the Elbow of his Left Arm,
This green waistcoat is laced with silver. In the Jean-Baptiste van Loo portraits you can see a embroidered silver waistcoat peeking out from beneath Hervey's coat.
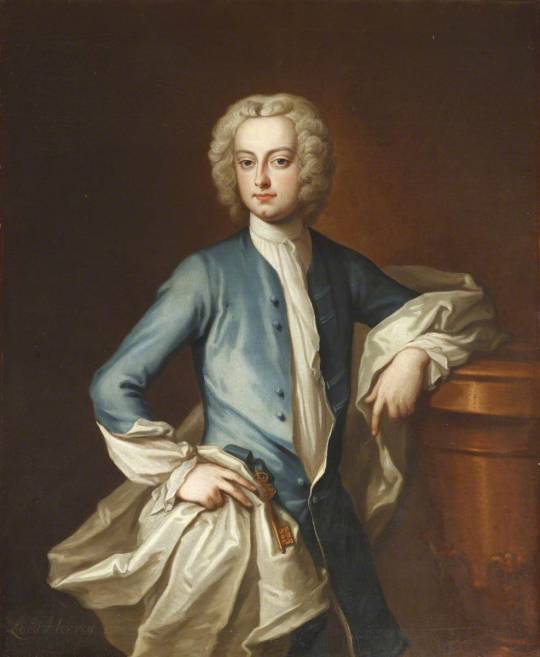
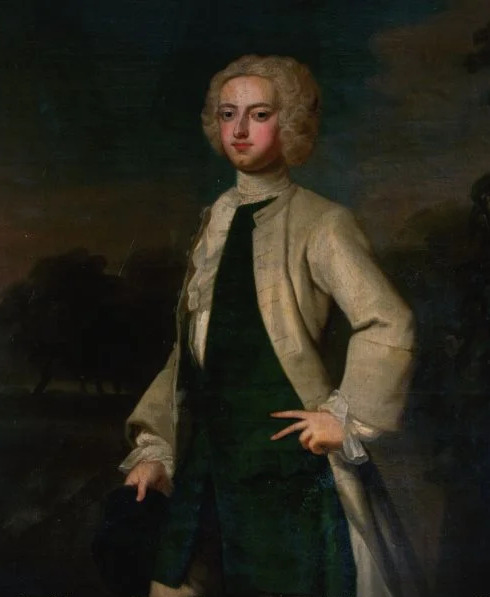


[Left: Lord John Hervey, oil on canvas, c.1737, by John Fayram, via Art UK.
Right: Lord John Hervey, oil on canvas, by Enoch Seeman, via The Collected Verse of John, Lord Hervey]
While the quality of the photo leaves much to be desired I wonder if the coat from the Seeman portrait is supposed to be silver. The coat he wears in the The Hervey Conversation Piece could also be silver but it might simply be grey. Sarah Osborn thought that silver coats looked effeminate. She wrote to Robert Byng on the 2nd of June 1722:
I believe the gentlemen will wear petticoats very soon, for many of their coats were like our mantuas. Lord Essex had a silver tissue coat, and pink color lutestring waistcoat, and several had pink color and pale blue paduasoy coats, which looked prodigiously effeminate.
Hervey wears a "prodigiously effeminate" pale blue, possibly paduasoy, coat (possibly a long sleeved waistcoat?) in the Fayram portrait.
The low buttoned waistcoat is somewhat interesting and consistent throughout his portraits, buttoned particularly low in the Fayram portrait. The effeminate Captain Whiffle from The Adventures of Roderick Random (1748) is described wearing his waistcoat "unbuttoned at the upper part to display a brooch set with garnets" but Hervey is broochless and looking at other portraits from this period the low buttoning doesn't seem to be unusual.
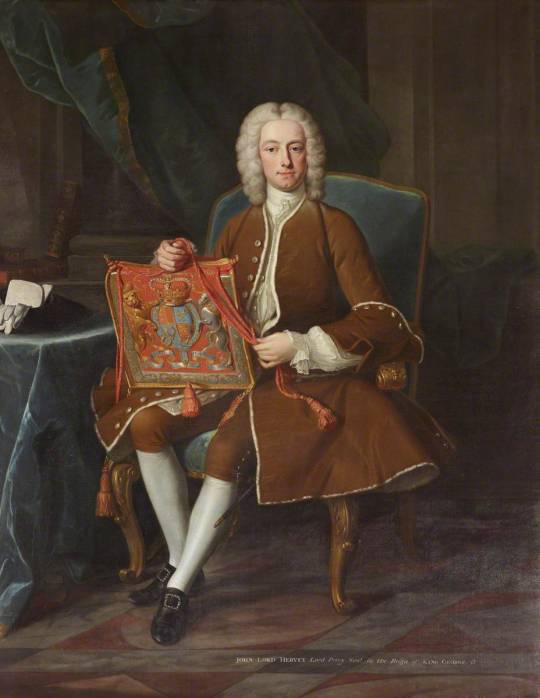


[Left: Detail of The Hervey Conversation Piece, oil on canvas, c.1738-40, by William Hogarth, via Fairfax House.
Right: Lord John Hervey, oil on canvas, c.1741, by Jean-Baptiste van Loo, via Art UK.]
Fur-lined suits like that worn by Hervey in the Jean-Baptiste van Loo portraits were imported from France or Italy and could be very costly. Mary Delany describes Lord Baltimore wearing "light brown and silver, his coat lined quite throughout with ermine" at a ball where "finery was so common it was hardly distinguished". (Mary Delany to Ann Granville, 22 Jan, 1739/40)
Fur-lined suits were somewhat of novelty in England and would become a feature in Grand Tour portraits. Peter McNeil explains in Pretty Gentleman (p123):
The novelty and glamour of new fashion goods generated excited responses to Lyons silk waistcoats, Italian velvets and fur-lined suits. There was a well-established tradition of wealthy men acquiring clothing on the continent and then having themselves painted in them, either in Italy or back in England.
(see Benjamin Lethieullier 1752, Lord Archibald Hamilton 1755-56 & John Scott 1774 all by Pompeo Batoni an artist well know for his Grand Tour portraits)
Hervey's buckles in the Jean-Baptiste van Loo portraits look to be set with paste (glass) or gems (buckles could even be set with diamonds). While it's impossible to tell what Hervey's buckles are set with these buckles could get very expensive. Later in the century macaroni were mocked for their expensive taste in similar buckles. (see McNeil p90)
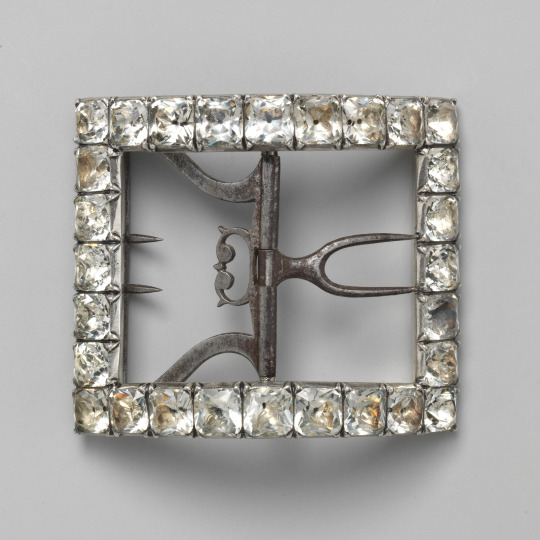


[Left: Shoe buckle, metal & paste, 18th century, British via The MET (83.1.103).
Right: Detail of Lord John Hervey, oil on canvas, c.1741, by Jean-Baptiste van Loo, via Art UK.]
While Hervey was certainly a fashionably dressed man he doesn't take it to the extent you might imagine of the archetypal fop. Satire exaggerates. Hervey's enemies chose their words deliberately to humiliate him. The amphibious thing of Pope's poetry was in reality a chronically ill queer man with a taste for fashion.
#I wrote this post while sick with covid so if anything doesn't make sense I blame the covid#lord hervey#queer history#fashion history
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
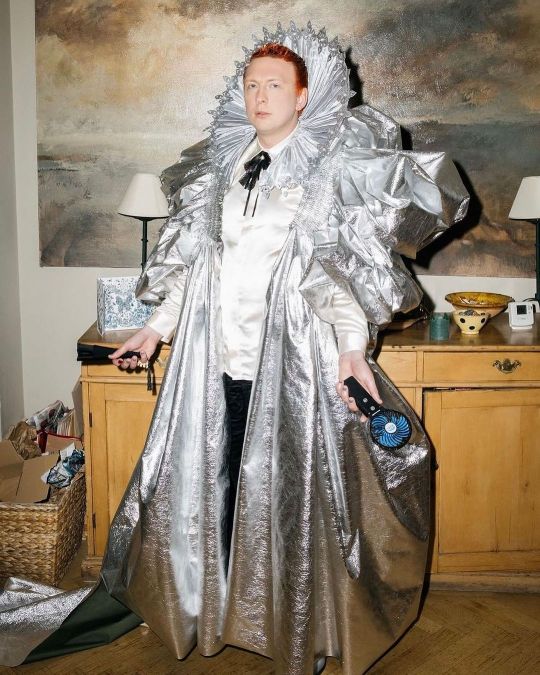

Joe Lycett as Elizabeth I, for the 2024 BAFTA Television Awards.
Gown by Yashana Malholtra, collar by Shoni, styled by Krishnan Parmar.
#joe lycett#as elizabeth i#elizabeth i#queen elizabeth i of england#portrayals#comedian#british tv#bafta television awards#2024#shoni#krishnan parmar#yashana malhotra#fashion#fashion history#red carpet#costume design
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
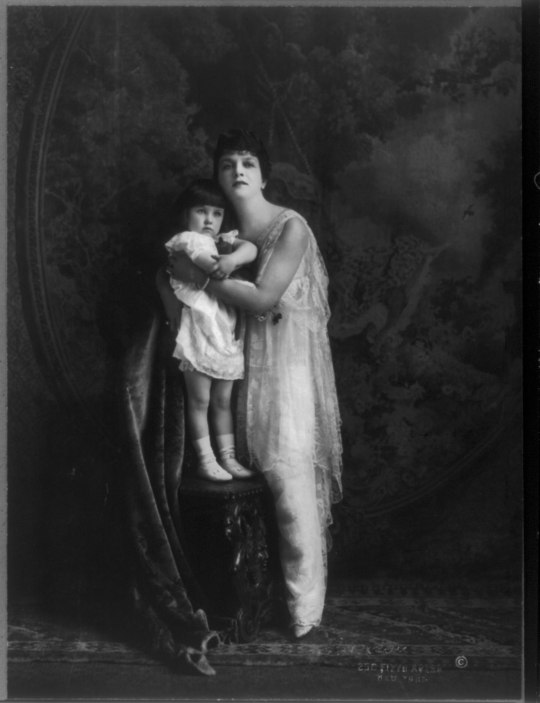

Edith Kingdon Gould and her daughter, 1915
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
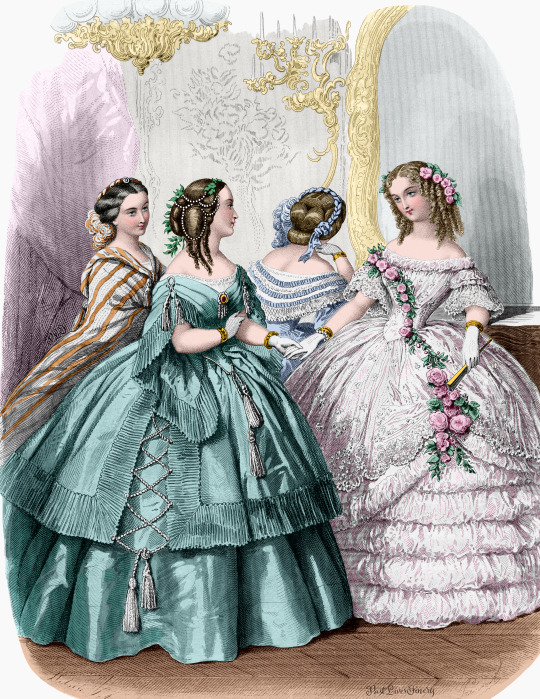
Le Bon Ton, 1858
#Le Bon Ton#1858#1850s#Victorian#Victoriana#Victorian fashion#Victorian dress#Victorian style#Victorian era#Victorian art#Victorian girl#Victorian woman#Fashion#Fashionplate#Fashion sketch#Fashion illustration#Fashion history#Historical fashion#Historical clothing#Dress history#Vintage dress#Vintage fashion#Antique dress#Antique fashion#Antique clothing#19th century#19th century style#19th century dress#19th century fashion#19th century art Corset
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
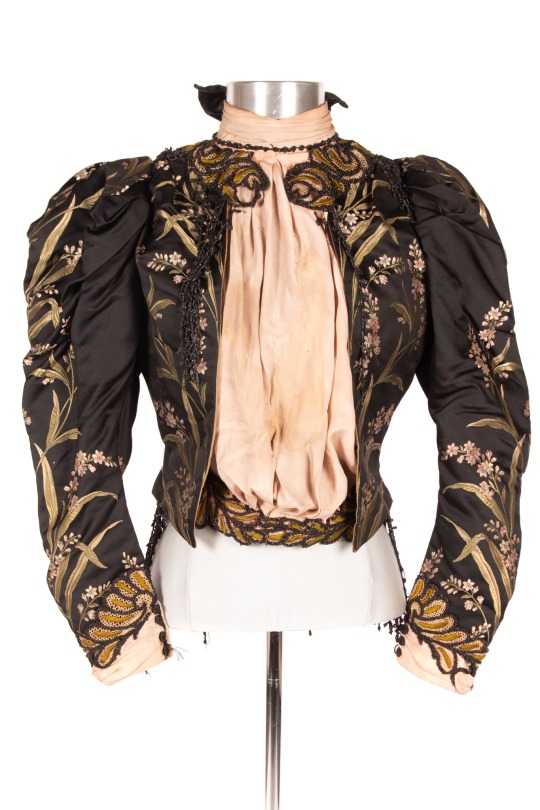
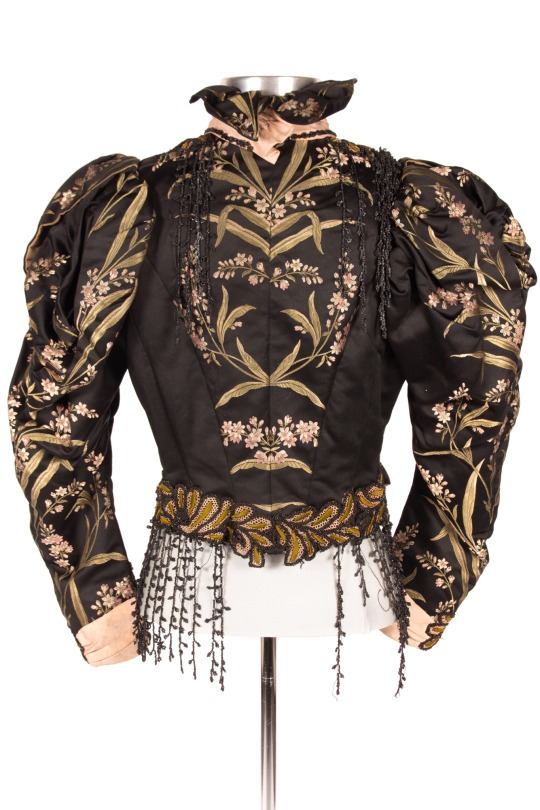


Bodice
circa 1880-1910
“This black bodice is made of silk and features floral embroidery throughout. It is boned and has a pink crepe panel down the center front and a standing collar as well as black bead trim throughout. There are also buttons on the cuffs and it has leg-of-mutton sleeves.”
Grand Rapids Public Museum
#god this is incredible#but that is such a huge gap in years omg#bodice#historical fashion#fashion history#history of fashion#historical clothing#vintage clothes#vintage clothing#vintage#frostedmagnolias
118 notes
·
View notes
Text
FWIW, "mauve" was one of the coal-tar dyes developed in the mid-19th century that made eye-wateringly bright clothing fashionable for a few decades.
It was an eye-popping magenta purple
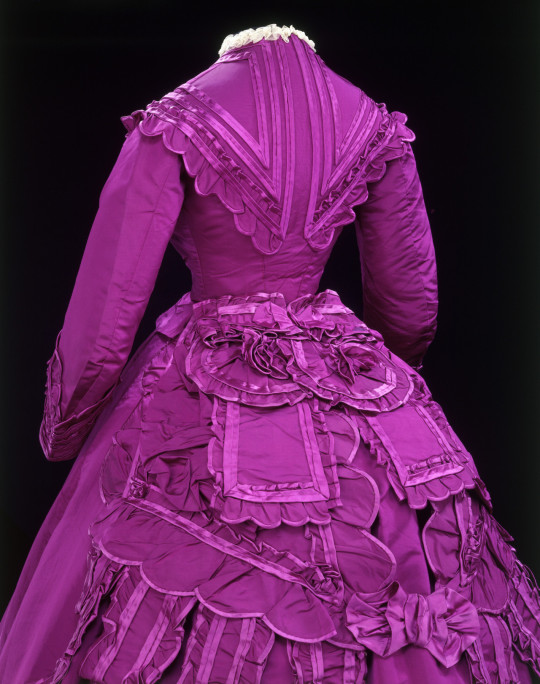

HOWEVER, like most aniline dyes, it faded badly, to a washed-out blue-grey ...
...which was the color ignorant youngsters in the 1920s associated with “mauve”.
(This dress is labeled "mauve" as it is the color the above becomes after fading).
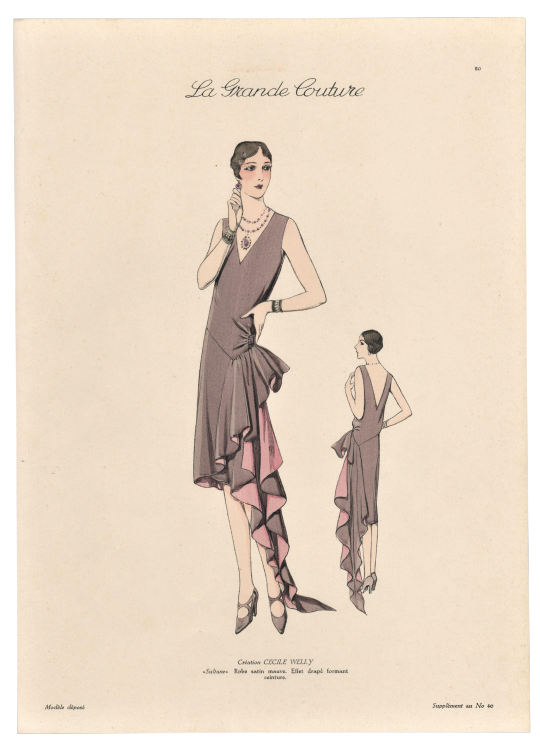

They colored their vision of the past with washed-out pastels that were NOTHING like the eye-popping electric shades the mid-Victorians loved. This 1926 fashion history book by Paul di Giafferi paints a hugely distorted, I would say dishonest picture of the past.

Ever since then this faded bluish lavender and not the original electric eye-watering hot pink-purple is the color associated with the word “mauve”.

22K notes
·
View notes
Text
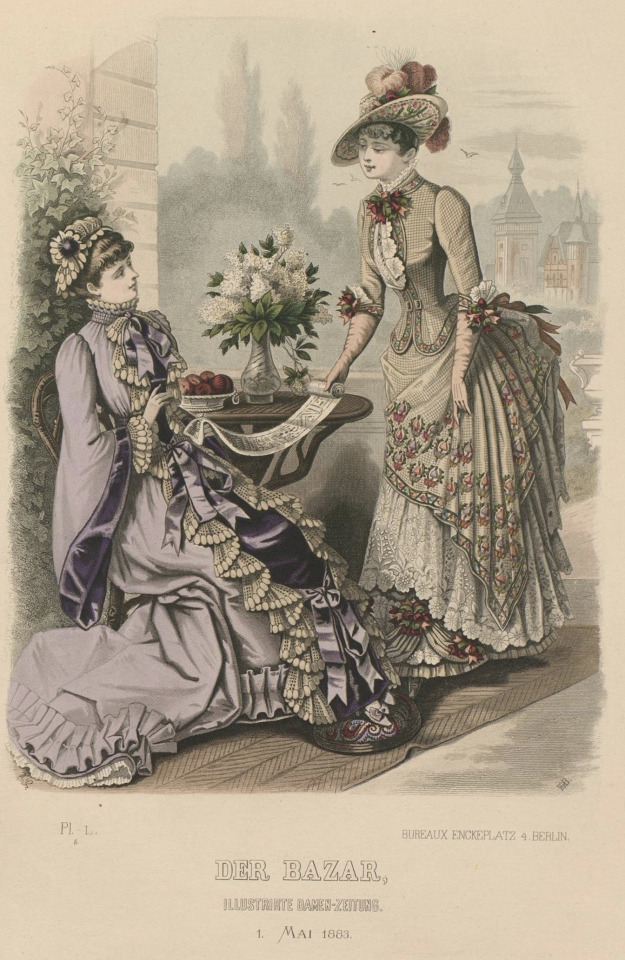

submitted by @edwardian-girl-next-door 💜🤎
#historical fashion poll submission#obsessed with the little footstool/cushion thing 😆#historical fashion polls#fashion poll#historical dress#historical fashion#dress history#fashion history#fashion plate#19th century#19th century fashion#19th century dress#late 19th century#1880s fashion#circa 1880#1880s dress#1880s#circa 1883#1883
64 notes
·
View notes
Text


solid perfume necklace in the shape of a mussel from estée lauder, 1974
27K notes
·
View notes
Text
I was about to be irritated at a shitty "kids' education" website on 1770s clothing but then I learned that there's a staymaker buried at King's Chapel and now I'm just delighted to know the gravesite of a clothing worker from that era and I want to take him flowers
10K notes
·
View notes